Secretory Peptides as Bullets: Effector Peptides from Pathogens against Antimicrobial Peptides from Soybean
- PMID: 33291499
- PMCID: PMC7730307
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239294
Secretory Peptides as Bullets: Effector Peptides from Pathogens against Antimicrobial Peptides from Soybean
Abstract
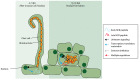
Soybean is an important crop as both human food and animal feed. However, the yield of soybean is heavily impacted by biotic stresses including insect attack and pathogen infection. Insect bites usually make the plants vulnerable to pathogen infection, which causes diseases. Fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes are major soybean pathogens. The infection by pathogens and the defenses mounted by soybean are an interactive and dynamic process. Using fungi, oomycetes, and bacteria as examples, we will discuss the recognition of pathogens by soybean at the molecular level. In this review, we will discuss both the secretory peptides for soybean plant infection and those for pathogen inhibition. Pathogenic secretory peptides and peptides secreted by soybean and its associated microbes will be included. We will also explore the possible use of externally applied antimicrobial peptides identical to those secreted by soybean and its associated microbes as biopesticides.
Keywords: antimicrobial; biopesticide; effector; endophyte; pathogen; rhizospheric microbe; secretory peptide; signaling; soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hartman G.L., West E.D., Herman T.K. Crops that feed the world 2. Soybean—Worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Sec. 2011;3:5–17. doi: 10.1007/s12571-010-0108-x. - DOI
-
- Nahashon S.N., Kilonzo-Nthenge A.K. Advances in soybean and soybean by-products in monogastric nutrition and health. In: El-Shemy H., editor. Soybean and Nutrition. InTech; Rijeka, Croatia: 2011. pp. 125–156.
-
- SoyStats. [(accessed on 10 September 2020)]; Available online: http://soystats.com/
-
- Verma S., Nizam S., Verma P. Biotic and abiotic stress signaling in plants. In: Sarwat M., Ahmad A., Abdin M.Z., editors. Stress Signaling in Plants: Genomics and Proteomics Perspective. Springer Science; New York, NY, USA: 2013. pp. 25–49.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

