Clinical Evaluation of Acetaminophen-Galgeuntang Interaction Based on Population Approaches
- PMID: 33291732
- PMCID: PMC7761965
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121182
Clinical Evaluation of Acetaminophen-Galgeuntang Interaction Based on Population Approaches
Abstract
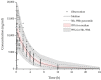
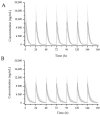
Galgeuntang (GGT), a traditional herbal medicine, is widely co-administered with acetaminophen (AAP) for treatment of the common cold, but this combination has not been the subject of investigation. Therefore, we investigated the herb-drug interaction between GGT and AAP by population pharmacokinetics (PKs) modeling and simulation studies. To quantify PK parameters and identify drug interactions, an open label, three-treatment, three-period, one-sequence (AAP alone, GGT alone, and AAP and GGT in combination) clinical trial involving 12 male healthy volunteers was conducted. Ephedrine (EPD), the only GGT component detected, was identified using a one-compartment model. The PKs of AAP were described well by a one-compartment model and exhibited two-phase absorption (rapid followed by slow) and first-order elimination. The model showed that EPD significantly influenced the PKs of AAP. The simulation results showed that at an AAP dose of 1000 mg × 4 times daily, the area under the concentration versus time curve of AAP increased by 16.4% in the presence of GGT compared to AAP only. In conclusion, the PKs of AAP were affected by co-administration of GGT. Therefore, when AAP is combined with GGT, adverse effects related to overdose of AAP could be induced possibly.
Keywords: Galgeuntang; acetaminophen; drug interaction; population pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yang T., Kim Y., Chae B. An experimental study on the anti-allergic effects, anti-inflammatory action, anti-pyretic action and analgesic action of Galgeun-tang, Gamigalgeun-tang and Geomahwanggalgeun-ang. J. Korean Orient. Med. Ophthalmol. Tolaryngol. Dermatol. 2002;15:1824.
-
- Shin J.-M., Kim Y.-O., Baek S.-H. Free radical scavenging activity and kinetic behavior of the Galgeuntang water extract. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2008;8:32–38. doi: 10.3742/OPEM.2008.8.1.032. - DOI
-
- Wu M.S., Yen H.R., Chang C.W., Peng T.Y., Hsieh C.F., Chen C.J., Lin T.Y., Horng J.T. Mechanism of action of the suppression of influenza virus replication by Ko-Ken Tang through inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and viral RNP nuclear export. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011;134:614–623. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.01.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ha H., Lee J.K., Lee M.-Y., Lim H.-S., Shin H. Galgeun-tang, an Herbal Formula, Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Responses in Dust Mite Extract-treated NC/Nga Mice. J. Korean Med. 2013;34:1–11. doi: 10.13048/jkm.13022. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

