Fluorescence-Based Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis and Flow Cytometry for Characterization of Endothelial Extracellular Vesicle Release
- PMID: 33291792
- PMCID: PMC7731108
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239278
Fluorescence-Based Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis and Flow Cytometry for Characterization of Endothelial Extracellular Vesicle Release
Abstract
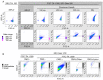
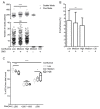
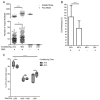
As extracellular vesicles (EVs) have become a prominent topic in life sciences, a growing number of studies are published on a regular basis addressing their biological relevance and possible applications. Nevertheless, the fundamental question of the true vesicular nature as well as possible influences on the EV secretion behavior have often been not adequately addressed. Furthermore, research regarding endothelial cell-derived EVs (EndoEVs) often focused on the large vesicular fractions comprising of microvesicles (MV) and apoptotic bodies. In this study we aimed to further extend the current knowledge of the influence of pre-isolation conditions, such as cell density and conditioning time, on EndoEV release from human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). We combined fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and the established fluorescence-triggered flow cytometry (FT-FC) protocol to allow vesicle-specific detection and characterization of size and surface markers. We found significant effects of cell density and conditioning time on both abundance and size distribution of EndoEVs. Additionally, we present detailed information regarding the surface marker display on EVs from different fractions and size ranges. Our data provide crucial relevance for future projects aiming to elucidate EV secretion behavior of endothelial cells. Moreover, we show that the influence of different conditioning parameters on the nature of EndoEVs has to be considered.
Keywords: endothelial cells; extracellular vesicles; fluorescence triggering flow cytometry; nano particle tracking.
Conflict of interest statement
J.G. is co-founder of Evercyte GmbH. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enumeration of extracellular vesicles by a new improved flow cytometric method is comparable to fluorescence mode nanoparticle tracking analysis.Nanomedicine. 2016 May;12(4):977-986. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.12.370. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26767510
-
Multicolor flow cytometry and nanoparticle tracking analysis of extracellular vesicles in the plasma of normal pregnant and pre-eclamptic women.Biol Reprod. 2013 Dec 26;89(6):151. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.113266. Print 2013 Dec. Biol Reprod. 2013. PMID: 24227753
-
Methods to Analyze EVs.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1545:1-20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6728-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27943203 Review.
-
Nitrite-derived nitric oxide reduces hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-mediated extracellular vesicle production by endothelial cells.Nitric Oxide. 2017 Feb 28;63:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Nitric Oxide. 2017. PMID: 28017872
-
Analysis of Individual Extracellular Vesicles by Flow Cytometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1678:79-92. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7346-0_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29071676 Review.
Cited by
-
Conditioning period impacts the morphology and proliferative effect of extracellular vesicles derived from rat adipose tissue derived stromal cell.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 4;23(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03273-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40033315 Free PMC article.
-
Cre mRNA Is Not Transferred by EVs from Endothelial and Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells during Vascular Network Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4050. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084050. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919955 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma and Laboratory Possibilities for Their Assessment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2273. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052273. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: An Effective Tool to Characterize Extracellular Vesicles.Molecules. 2024 Oct 1;29(19):4672. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194672. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterisation of Extracellular Vesicles from Equine Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 23;23(10):5858. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105858. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628667 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

