The Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Type A (BoNT-A) Treatment in Brazilian Patients with Chronic Post-Stroke Spasticity: Results from the Observational, Multicenter, Prospective BCause Study
- PMID: 33291807
- PMCID: PMC7762077
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12120770
The Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Type A (BoNT-A) Treatment in Brazilian Patients with Chronic Post-Stroke Spasticity: Results from the Observational, Multicenter, Prospective BCause Study
Abstract
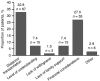
Botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) is an effective treatment for post-stroke spasticity; however, some patients cannot access treatment until ≥1 year post-stroke. This Brazilian post-marketing study (NCT02390206) assessed the achievement of person-centered goals in patients with chronic post-stroke spasticity after a BoNT-A injection. Patients had a last documented stroke ≥1 year before study entry and post-stroke upper limb (UL) spasticity, with or without lower limb (LL) spasticity. Patients received BoNT-A injections at baseline (visit 1) and visit 2 (3-6 months). Primary endpoint was responder rate (achievement of primary goal from Goal Attainment Scaling (GAS)) at visit 2. Overall, 204 patients underwent GAS evaluation at visit 2, mean (SD) age was 56.4 (13.2) years and 90.7% had LL spasticity. Median (range) time between first stroke and onset of spasticity was 3.6 (0-349) months, onset of spasticity and first injection was 22.7 (0-350) months and waiting time for a rehabilitation appointment was 9.0 (1-96) months. At visit 2, 61.3% (95% CI: 54.4, 67.7) of patients were responders, which was similar for UL and LL primary goals (57.8% [95% CI: 49.9, 65.3] vs. 64.1% [95% CI: 48.4, 77.3]). This study provides evidence to support the effectiveness of BoNT-A treatment for chronic post-stroke spasticity.
Keywords: pain; quality of life; spasticity; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
P.K.: received consultancy fees from Ipsen and Allergan, and honorarium as a speaker from Ipsen and Allergan. M.R.: supported by Ipsen, Allergan and Merz in scientific events as a speaker or participant. J.A.F.: sponsored by Ipsen and Allergan. R.C.: sponsored by Ipsen and Merz in scientific events as a speaker or participant. A.C.F.G.A.: sponsored by Ipsen, Allergan, Merz to attend scientific meetings, and has received funds as an instructor for Dysport. D.X.: received fees from Ipsen and Allergan. T.M.C.: no conflicting interests. L.H.C.M.: supported Ipsen, Allergan and Merz as a speaker for presentations and workshops about botulinum toxin and chemical blockade; sponsored by Ipsen and Merz to attend scientific meetings. A.L.L.: no conflicting interests. S.L.: no conflicting interests. P.M.: employee of Ipsen. V.C.R.-S.: employee of Ipsen at the time this research was carried out.
Figures



References
-
- Simpson D.M., Hallett M., Ashman E.J., Comella C.L., Green M.W., Gronseth G.S., Armstrong M.J., Gloss D., Potrebic S., Jankovic J., et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2016;86:1818–1826. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

