Benchmark Sets for Binding Hot Spot Identification in Fragment-Based Ligand Discovery
- PMID: 33291870
- PMCID: PMC8200320
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00877
Benchmark Sets for Binding Hot Spot Identification in Fragment-Based Ligand Discovery
Abstract
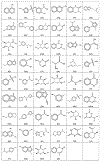
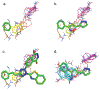
Binding hot spots are regions of proteins that, due to their potentially high contribution to the binding free energy, have high propensity to bind small molecules. We present benchmark sets for testing computational methods for the identification of binding hot spots with emphasis on fragment-based ligand discovery. Each protein structure in the set binds a fragment, which is extended into larger ligands in other structures without substantial change in its binding mode. Structures of the same proteins without any bound ligand are also collected to form an unbound benchmark. We also discuss a set developed by Astex Pharmaceuticals for the validation of hot and warm spots for fragment binding. The set is based on the assumption that a fragment that occurs in diverse ligands in the same subpocket identifies a binding hot spot. Since this set includes only ligand-bound proteins, we added a set with unbound structures. All four sets were tested using FTMap, a computational analogue of fragment screening experiments to form a baseline for testing other prediction methods, and differences among the sets are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure:
Acpharis Inc. offers commercial licenses to ATLAS, a software product in function similar to FTMap. Dima Kozakov and Sandor Vajda owns stock in the company. However, the FTMap program and the use of the FTMap server are free for academic and governmental use.
Figures

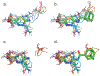


References
-
- Clackson T; Wells JA, A hot spot of binding energy in a hormone-receptor interface. Science 1995, 267, 383–386. - PubMed
-
- Thanos CD; Randal M; Wells JA, Potent small-molecule binding to a dynamic hot spot on IL-2. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2003, 125, 15280–15281. - PubMed
-
- Allen KN; Bellamacina CR; Ding XC; Jeffery CJ; Mattos C; Petsko GA; Ringe D, An experimental approach to mapping the binding surfaces of crystalline proteins. J. Phys. Chem 1996, 100, 2605–2611.
-
- Mattos C; Ringe D, Locating and characterizing binding sites on proteins. Nat. Biotechnol 1996, 14, 595–599. - PubMed
-
- English AC; Groom CR; Hubbard RE, Experimental and computational mapping of the binding surface of a crystalline protein. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 47–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

