The isolated La-module of LARP1 mediates 3' poly(A) protection and mRNA stabilization, dependent on its intrinsic PAM2 binding to PABPC1
- PMID: 33292040
- PMCID: PMC7928023
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1860376
The isolated La-module of LARP1 mediates 3' poly(A) protection and mRNA stabilization, dependent on its intrinsic PAM2 binding to PABPC1
Abstract
The protein domain arrangement known as the La-module, comprised of a La motif (LaM) followed by a linker and RNA recognition motif (RRM), is found in seven La-related proteins: LARP1, LARP1B, LARP3 (La protein), LARP4, LARP4B, LARP6, and LARP7 in humans. Several LARPs have been characterized for their distinct activity in a specific aspect of RNA metabolism. The La-modules vary among the LARPs in linker length and RRM subtype. The La-modules of La protein and LARP7 bind and protect nuclear RNAs with UUU-3' tails from degradation by 3' exonucleases. LARP4 is an mRNA poly(A) stabilization factor that binds poly(A) and the cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding protein PABPC1 (also known as PABP). LARP1 exhibits poly(A) length protection and mRNA stabilization similar to LARP4. Here, we show that these LARP1 activities are mediated by its La-module and dependent on a PAM2 motif that binds PABP. The isolated La-module of LARP1 is sufficient for PABP-dependent poly(A) length protection and mRNA stabilization in HEK293 cells. A point mutation in the PAM2 motif in the La-module impairs mRNA stabilization and PABP binding in vivo but does not impair oligo(A) RNA binding by the purified recombinant La-module in vitro. We characterize the unusual PAM2 sequence of LARP1 and show it may differentially affect stable and unstable mRNAs. The unique LARP1 La-module can function as an autonomous factor to confer poly(A) protection and stabilization to heterologous mRNAs.
Keywords: La motif, poly(A)-binding protein; La-related protein; RNA recognition motif; poly(A) tail.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
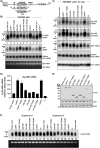
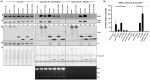

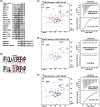
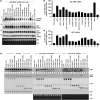
References
-
- Craig AW, Haghighat A, Yu AT, et al. Interaction of polyadenylate-binding protein with the eIF4G homologue PAIP enhances translation. Nature. 1998;392:520–523. - PubMed
-
- Uchida N, Hoshino S, Imataka H, et al. A novel role of the mammalian GSPT/eRF3 associating with poly(A)-binding protein in Cap/Poly(A)-dependent translation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:50286–50292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
