Screening of Multiple Biomarkers Associated With Ischemic Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 33292046
- PMCID: PMC7955358
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018984
Screening of Multiple Biomarkers Associated With Ischemic Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
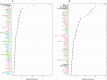
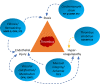
Background To explore the pathophysiological features of ischemic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), we evaluated the association between 268 plasma proteins and subsequent ischemic stroke in 2 large AF cohorts receiving oral anticoagulation. Methods and Results A case-cohort sample of patients with AF from the ARISTOTLE (Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation) trial, including 282 cases with ischemic stroke or systemic embolism and a random sample of 4124 without these events, during 1.9 years of follow-up was used for identification. Validation was provided by a similar case-cohort sample of patients with AF from the RE-LY (Randomized Evaluation of Long-Term Anticoagulation Therapy) trial, including 149 cases with ischemic stroke/systemic embolism and a random sample of 1062 without these events. In plasma obtained before randomization, 268 unique biomarkers were measured with OLINK proximity extension assay panels (CVD II, CVD III, and Inflammation) and conventional immunoassays. The association between biomarkers and outcomes was evaluated by random survival forest and adjusted Cox regression. According to random survival forest or Cox regression analyses, the biomarkers most strongly and consistently associated with ischemic stroke/systemic embolism were matrix metalloproteinase-9, NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide), osteopontin, sortilin, soluble suppression of tumorigenesis 2, and trefoil factor-3. The corresponding hazard ratios (95% CIs) for an interquartile difference were as follows: 1.18 (1.00-1.38), 1.55 (1.28-1.88), 1.28 (1.07-1.53), 1.19 (1.02-1.39), 1.23 (1.05-1.45), and 1.19 (0.97-1.45), respectively. Conclusions In patients with AF, of 268 unique biomarkers, the 6 biomarkers most strongly associated with subsequent ischemic stroke/systemic embolism represent fibrosis/remodeling (matrix metalloproteinase-9 and soluble suppression of tumorigenesis 2), cardiac dysfunction (NT-proBNP), vascular calcification (osteopontin), metabolism (sortilin), and mucosal integrity/ischemia (trefoil factor-3). Registration URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique Identifiers: NCT00412984 and NCT00262600.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; biomarkers; ischemic stroke; pathophysiological features; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Hijazi has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Pfizer, and consulting fees from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Roche, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Pfizer. The growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF‐15) assays were provided by Roche. Dr Wallentin has received institutional research grants, consultancy fees, lecture fees, and travel support from Bristol‐Myers Squibb/Pfizer, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr Wallentin also received institutional research grants from Merck & Co and Roche, received consultancy fees from Abbott, and holds 2 patents involving GDF‐15. J. Lindbäck received institutional research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol‐Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Dr Alexander has received institutional research grants, consulting fees, and honoraria from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Regado Biosciences, and Merck, and consulting fees and honoraria from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ortho‐McNeil‐Janssen, Polymedix, and Bayer. Dr Connolly has received consulting fees, speaker fees, and research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Bayer, and Portola, consulting fees and research grants from Sanofi‐Aventis, and research grants from Boston Scientific. Dr Eikelboom has received institutional research grants and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Daiichi‐Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Glaxo Smith Kline, Janssen, and Sanofi. Dr Ezekowitz has received grants and consultant fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers‐Squibb, and Pfizer, and consultant fees from Boston Scientific, Anthos Therapeutic, and Alta Therapeutics. Dr Granger has received grants and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Sanofi‐Aventis, Takeda, The Medicines Company, Janssen, Bayer, and Hoffmann‐La Roche, grants from Medtronics Foundation, Merck & Co, and Armetheon, and personal fees from Lilly, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Ross Medical Corporation, Salix Pharmaceuticals, and Gilead. Dr Lopes has received an institutional research grant and consulting fees from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, an institutional research grant from GlaxoSmithKline, and consulting fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingleheim, Pfizer, Merck, and Portola. Dr Yusuf has received grants, speaker fees, and paid travel expenses from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr Oldgren has received consulting and lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Pfizer. Dr Siegbahn has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb/Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Roche Diagnostics, and consulting fees from OLINK Proteomics. Dr Pol has no disclosures to report.
Figures

References
-
- Kirchhof P, Breithardt G, Aliot E, Al Khatib S, Apostolakis S, Auricchio A, Bailleul C, Bax J, Benninger G, Blomstrom‐Lundqvist C, et al. Personalized management of atrial fibrillation: proceedings from the fourth Atrial Fibrillation competence NETwork/European Heart Rhythm Association consensus conference. Europace. 2013;15:1540–1556. 10.1093/europace/eut232 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hijazi Z, Lindbäck J, Alexander JH, Hanna M, Held C, Hylek EM, Lopes RD, Oldgren J, Siegbahn A, Stewart RAH, et al. The ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history) stroke risk score: a biomarker‐based risk score for predicting stroke in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1582–1590. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw054 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

