LncRNA SNHG3, a potential oncogene in human cancers
- PMID: 33292213
- PMCID: PMC7640707
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01608-x
LncRNA SNHG3, a potential oncogene in human cancers
Abstract
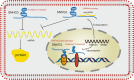
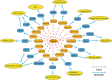
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are composed of > 200 nucleotides; they lack the ability to encode proteins but play important roles in a variety of human tumors. A large number of studies have shown that dysregulated expression of lncRNAs is related to tumor oncogenesis and progression. Emerging evidence shows that SNHG3 is a novel oncogenic lncRNA that is abnormally expressed in various tumors, including osteosarcoma, liver cancer, lung cancer, etc. SNHG3 primarily competes as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) that targets tumor suppressor microRNAs (miRNAs) and ceRNA mechanisms that regulate biological processes of tumors. In addition, abnormal expression of SNHG3 is significantly correlated with patient clinical features. Upregulation of SNHG3 contributes to biological functions, including tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT. Therefore, SNHG3 may represent a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker, as well as a novel therapeutic target.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; LncRNA; SNHG3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the ceRNA network mediated by lncRNA SNHG3 in the progression of cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 30;15(1):514. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01184-w. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39349640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 functions as a novel biomarker in liver cancer and other tumour progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 28;28(16):1641-1655. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i16.1641. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35581965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA SNHG3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through the miR-384/hepatoma-derived growth factor axis in breast cancer.Hum Cell. 2020 Jan;33(1):232-242. doi: 10.1007/s13577-019-00287-9. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 31586299
-
LncRNA SNHG3 promotes cell growth by sponging miR-196a-5p and indicates the poor survival in osteosarcoma.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019 Jan-Dec;33:2058738418820743. doi: 10.1177/2058738418820743. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30791797 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SNHG3 Promotes Hepatocellular Tumorigenesis by Targeting miR-326.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019 Sep;249(1):43-56. doi: 10.1620/tjem.249.43. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31548493
Cited by
-
Prognostic signature of lipid metabolism associated LncRNAs predict prognosis and treatment of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 1;12:986367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.986367. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387240 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the lncRNA NBR2 on the proliferation and autophagy of breast cancer cells under starvation conditions.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 30;14(1):22624. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72181-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39349960 Free PMC article.
-
lncSNHG3 drives breast cancer progression by epigenetically increasing CSNK2A1 expression level.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jun 21;15(12):5734-5750. doi: 10.18632/aging.204824. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37348024 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of competing endogenous RNA and associated noncoding RNAs in thyroid cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 15;12(3):961-973. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35411240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA SNHG3 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of human thyroid cancer via miR-339-5p/GPR62 axis.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 1;9(9):e19713. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19713. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Niksic M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ, Esteve J, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391(10125):1023–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

