Geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor of complications and long-term outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33292289
- PMCID: PMC7603782
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01628-7
Geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor of complications and long-term outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The effect of the geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI) on the prognosis of patients with gastrointestinal malignancy remains unclear. The aim of our study was to systematically explore the value of the GNRI in evaluating postoperative complications and long-term outcomes in gastrointestinal malignancy.
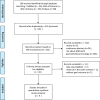
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted using electronic databases to report the impact of the GNRI on postoperative complications and long-term outcomes of patients with gastrointestinal malignancies as of August 2020. The hazard ratio (HR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to evaluate the impact of the GNRI on long-term outcomes. The risk ratio (RR) with 95% CI was used to assess the impact of the GNRI on postoperative complications.
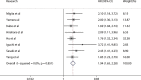
Result: A total of nine studies with 2,153 patients were enrolled in our meta-analysis. The results suggested that a low GNRI was correlated with poor overall survival of patients with gastrointestinal malignancy (HR = 1.94, 95% CI 1.65-2.28, p < 0.001). Patients with a low GNRI had a higher risk of complications than patients with a high GNRI (OR = 2.19, 95% CI 1.57-3.05, p < 0.001). In addition, patients with a low GNRI had shorter relapse-free survival (HR = 2.45, 95% CI 1.50-4.00, p < 0.001) and disease-free survival (HR = 1.84, 95% CI 1.23-2.76, p = 0.003) than those with a high GNRI. However, the GNRI was not an independent factor affecting cancer-specific survival (HR = 1.60, 95% CI 0.91-2.82, p = 0.101).
Conclusion: Based on existing evidence, the GNRI was a valuable predictor of complications and long-term outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy.
Keywords: Complications; Gastrointestinal malignancy; Geriatric nutritional risk index; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor for postoperative complications in patients with solid cancers: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 7;14:1266291. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1266291. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38384816 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of postoperative complications and survival after laparoscopic gastrectomy using preoperative Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in elderly gastric cancer patients.Surg Endosc. 2021 Mar;35(3):1202-1209. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07487-7. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Surg Endosc. 2021. PMID: 32152675
-
Predictive Value of Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Nutr Cancer. 2023;75(1):24-32. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2115521. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Nutr Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36039473
-
Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Adverse Outcomes in Human Malignancy: A Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2019 Nov 19;2019:4796598. doi: 10.1155/2019/4796598. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31827634 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of preoperative geriatric nutritional risk index for clinical outcomes in surgical gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2022 Nov 2;9:1020482. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1020482. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36406367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Low Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Is Associated with Low Muscle Volume and a Poor Prognosis among Cirrhotic Patients.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 29;59(12):2099. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122099. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138202 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of geriatric nutritional risk index for aspiration pneumonia: a retrospective observational cohort study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 Mar;34(3):563-571. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-01948-2. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 34379292
-
The prognostic effects of the geriatric nutritional risk index on elderly acute kidney injury patients in intensive care units.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 11;10:1165428. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1165428. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37250638 Free PMC article.
-
The geriatric nutritional risk index predicts complications after nephrectomy for renal cancer.Int Braz J Urol. 2023 Jan-Feb;49(1):97-109. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2022.0380. Int Braz J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36512458 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of the combination of body composition and systemic inflammation in patients with cancer cachexia.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Apr;14(2):879-890. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13205. Epub 2023 Mar 5. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 36872512 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

