Relationship between pre- and post-operative isokinetic strength after ACL reconstruction using hamstring autograft
- PMID: 33292502
- PMCID: PMC7602313
- DOI: 10.1186/s13102-020-00215-7
Relationship between pre- and post-operative isokinetic strength after ACL reconstruction using hamstring autograft
Abstract
Background: Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) ruptures are of major concern in sports. As mostly young and active individuals are affected there is an emphasis on the rapid and safe return to sports (RTS). Strengthening the ventral and dorsal thigh muscles is a prerequisite for a successful RTS after ACL reconstruction (ACLR), as persistent muscle weakness may increase the incidence for secondary injuries and impair performance. Aiming to increase evidence on the importance of preoperative muscle strength and the coaching of patients, the purpose of this study is to compare thigh muscle strength pre- and post-operatively after ACLR.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of 80 patients with primary, isolated ACLR using a four-stranded hamstring autograft. We performed bilateral isokinetic concentric strength measurement (60°/s) before and six months after ACLR. Primary outcomes were the maximal knee extension and flexion torque, hamstrings-to-quadriceps ratio (H/Q ratio) and the corresponding limb symmetry indices (LSI). Pearson correlations were calculated for pre- and post-surgical values.
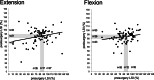
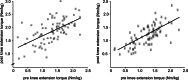
Results: The operated as well as the unaffected leg increased maximal knee extension (+ 18% ± 7% p < 0.05; + 11% ± 5% p < 0.05) and flexion torque (+ 9% ± 5% p < 0.05, + 10% ± 6% p < 0.05) throughout the 6 months of rehabilitation. The H/Q ratio remained unaffected (- 2% ± 3% p = 0.93; - 4% ± 4% p = 0.27). LSI of knee extension strength increased significantly (6% ± 3% p < 0.05), while flexion strength remained unaffected (+ 2% ± 4% p = 0.27). Positive correlations underline the interrelationship between the strength pre- and post-surgery for the knee extension (r = 0.788 p < 0.05) and knee flexion strength (r = 0.637 p < 0.05) after ACLR.
Conclusions: Preoperative leg extension and flexion strength normalized to body mass are strongly correlated to postoperative strength performance after ACLR. Therefore, pre-operative quadriceps and hamstring muscle strength deficits may have a significant negative impact on functional performance following ACLR. This emphasizes the need for intensive preoperative screening and subsequent treatment to achieve the best possible preoperative leg strength before ACLR.
Trial registration: DRKS00020210 .
Keywords: ACL reconstruction; Isokinetic strength measurements; Pre-habilitation; Return to sport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ardern CL, Webster KE, Taylor NF, Feller JA. Return to sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the state of play. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(7):596–606. - PubMed
-
- Zwolski C, Schmitt LC, Thomas S, Hewett TE, Paterno MV. The utility of limb symmetry indices in return-to-sport assessment in patients with bilateral anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(8):2030–2038. - PubMed
-
- Petersen W, Fink C, Kopf S. Return to sports after ACL reconstruction: a paradigm shift from time to function. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(5):1353–1355. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

