A novel point-of-care device for measuring glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency
- PMID: 33293060
- PMCID: PMC7856170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semperi.2020.151356
A novel point-of-care device for measuring glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency
Abstract
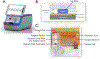
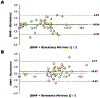
Extreme hyperbilirubinemia can cause bilirubin neurotoxicity. Infants with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency can develop hemolysis and thus are at high risk. We evaluated a device that quantitatively measures G6PD activity kinetically using digital microfluidics (DMF). Intra- and inter-instrument and -day imprecision (CVs) were first assessed. G6PD activity in 86 samples was then measured and compared between DMF and 2 reference methods. Overall DMF reproducibility was 3.8% over 5 days by 2 operators on 2 instruments. Mean intra- and inter-instrument variabilities were 3.6% and 3.9%, respectively (n = 28), with a user variability of 4.3%. Mean G6PD activity was 6.40±4.62 and 6.37±4.62 U/g hemoglobin for DMF and Reference Methods 1 (n = 46) and 12.15±3.86 and 11.48±1.55 for DMF and 2 (n = 40), respectively, and strongly correlated (r = 0.95 and 0.95) with mean biases of +0.04±2.90 and +0.67±1.55 for methods 1 and 2, respectively. The novel device could be used for early newborn G6PD screening.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
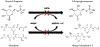
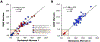
References
-
- Beutler E Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:169–174. - PubMed
-
- Cappellini MD, Fiorelli G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet. 2008;371:64–74. - PubMed
-
- Valaes T, Karaklis A, Stravrakakis D, et al. Incidence and mechanism of neonatal jaundice related to glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1969;3:448–458. - PubMed
-
- Johnson L, Bhutani VK, Karp K, Sivieri E, Shapiro S. Clinical report from the pilot USA Kernicterus Registry (1992 to 2004). J Perinatol. 2009;29:S25–S45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

