Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
- PMID: 33293564
- PMCID: PMC7722853
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20061-y
Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Abstract
Advances in farming technology and intensification of animal agriculture increase the cost-efficiency and production volume of meat. Thus, in developed nations, meat is relatively inexpensive and accessible. While beneficial for consumer satisfaction, intensive meat production inflicts negative externalities on public health, the environment and animal welfare. In response, groups within academia and industry are working to improve the sensory characteristics of plant-based meat and pursuing nascent approaches through cellular agriculture methodology (i.e., cell-based meat). Here we detail the benefits and challenges of plant-based and cell-based meat alternatives with regard to production efficiency, product characteristics and impact categories.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
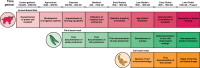

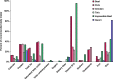
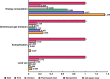
References
-
- Godfray, H. C. J. et al. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science361, eaam5324 (2018). Global meat consumption, driven upward by economic prosperity and population growth, negatively impacts human health and the environment. - PubMed
-
- Alexandratos, N. & Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision. Agricultural Development Economics Division (2012).
-
- Waite, R. et al. Improving productivity and environmental performance of aquaculture. Creating a Sustainable Food Future. 10.5657/FAS.2014.0001 (2014).
-
- Vranken L, Avermaete T, Petalios D, Mathijs E. Curbing global meat consumption: emerging evidence of a second nutrition transition. Environ. Sci. Policy. 2014;39:95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2014.02.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

