MicroRNA-155 contributes to plexiform neurofibroma growth downstream of MEK
- PMID: 33293695
- PMCID: PMC7867646
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-01581-9
MicroRNA-155 contributes to plexiform neurofibroma growth downstream of MEK
Abstract
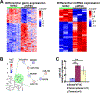
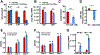
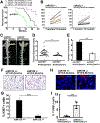
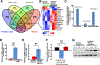
MicroRNAs (miRs) are small non-coding RNAs that can have large impacts on oncogenic pathways. Possible functions of dysregulated miRs have not been studied in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) plexiform neurofibromas (PNFs). In PNFs, Schwann cells (SCs) have biallelic NF1 mutations necessary for tumorigenesis. We analyzed a miR microarray comparing with normal and PNF SCs and identified differences in miR expression, and we validated in mouse PNFs versus normal mouse SCs by qRT-PCR. Among these, miR-155 was a top overexpressed miR, and its expression was regulated by RAS/MAPK signaling. Overexpression of miR-155 increased mature Nf1-/- mouse SC proliferation. In SC precursors, which model tumor-initiating cells, pharmacological and genetic inhibition of miR-155 decreased PNF-derived sphere numbers in vitro, and we identified Maf as a miR-155 target. In vivo, global deletion of miR-155 significantly decreased tumor number and volume, increasing mouse survival. Fluorescent nanoparticles entered PNFs, suggesting that an anti-miR might have therapeutic potential. However, treatment of established PNFs using anti-miR-155 peptide nucleic acid-loaded nanoparticles marginally decreased tumor numbers and did not reduce tumor growth. These results suggest that miR-155 plays a functional role in PNF growth and/or SC proliferation, and that targeting neurofibroma miRs is feasible, and might provide novel therapeutic opportunities.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

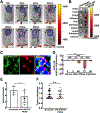
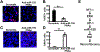
References
-
- Varan A, Sen H, Aydin B, Yalcin B, Kutluk T, Akyuz C. Neurofibromatosis type 1 and malignancy in childhood. Clin Genet. 2016;89(3):341–5. - PubMed
-
- Rice FL, Houk G, Wymer JP, Gosline SJC, Guinney J, Wu J, et al. The evolution and multi-molecular properties of NF1 cutaneous neurofibromas originating from C-fiber sensory endings and terminal Schwann cells at normal sites of sensory terminations in the skin. PloS One. 2019;14(5):e0216527. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

