Application of Carbon Nanoparticles in Tracing Lymph Nodes and Locating Tumors in Colorectal Cancer: A Concise Review
- PMID: 33293812
- PMCID: PMC7719328
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S281914
Application of Carbon Nanoparticles in Tracing Lymph Nodes and Locating Tumors in Colorectal Cancer: A Concise Review
Abstract
Background: Accurate lymph node (LN) staging has considerably prognostic and therapeutic value in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). The purpose of this study is to evaluate the feasibility of applying carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) to track LN metastases in CRC.
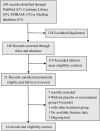
Methods: Two researchers independently screened publications in PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane and Ovid MEDLINE databases. The keywords were (carbon nanoparticles OR activated carbon nanoparticles) AND (colon cancer OR rectal cancer OR colorectal cancer). Titles and abstracts of the articles were meticulously read to rule out potential publications. Next, full texts of the ultimately obtained eligible publications were retrieved and analyzed in detail.
Results: The search produced 268 publications, and 140 abstracts were identified after a bibliographic review. Finally, 20 studies relevant to our subject were obtained; however, only 14 papers met our inclusion criteria and were included for final review. All studies included have compared the control group with carbon nanoparticles group (control group, defined as nontattooed group; and carbon nanoparticles group, defined as administering carbon nanoparticles during surgery) for their efficacy in intraoperative detecting and positioning. After analysis, appreciably less amount of bleeding (3/5 trials), shorter operation time (2/4 trials), and shorter time to detect lesions and dissect LNs (2/2 trials) were revealed in CNPs group compared to control group. Thirteen studies have recorded the numbers of the harvested LNs in both groups; meanwhile, CNPs group shows superiority to control group in LN retrieval as well (11/13 trials), which also could effectively aid in locating and harvesting more LNs with diameter below 5 mm.
Conclusion: The tracing technique for CNPs is a safe and useful strategy both in localizing tumor and tracing LNs in CRC surgery. But there is still a need for more randomized controlled trials to further establish its contribution to patient survival.
Keywords: carbon nanoparticles; colorectal cancer; lymph nodes; trace; tumor location.
© 2020 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Similar articles
-
Clinical study of harvesting lymph nodes with carbon nanoparticles in advanced gastric cancer: a prospective randomized trial.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Mar 24;14:88. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0835-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27009101 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The prognostic value of lymph node yield in the earliest stage of colorectal cancer: a multicenter cohort study.BMC Med. 2017 Jul 14;15(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0892-7. BMC Med. 2017. PMID: 28705200 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of carbon nanoparticles in lymphatic mapping during colorectal cancer surgeries: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Dig Liver Dis. 2020 Dec;52(12):1445-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.08.020. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Dig Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 32912769
-
Methylene blue can increase the number of lymph nodes harvested in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2023 Feb 18;38(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00384-023-04312-0. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2023. PMID: 36807534 Review.
-
Preoperative endoscopic localization of colorectal cancer and tracing lymph nodes by using carbon nanoparticles in laparoscopy.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Aug 30;14(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0987-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27577559 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of carbon nanoparticles staining on lymph node tracking in colorectal cancer: A propensity score matching analysis.Front Surg. 2023 Mar 1;10:1113659. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1113659. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36936663 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodrugs systems for therapy and diagnosis of esophageal cancer.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 13;11:1233476. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1233476. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37520291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From organ preservation to selective surgery: How immunotherapy changes colorectal surgery?Surg Open Sci. 2023 Aug 9;15:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.sopen.2023.07.024. eCollection 2023 Sep. Surg Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 37637243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-assisted carbon nanoparticle labeling of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast-conserving surgery in breast cancer.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):1825-1837. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-361. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915352 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-draining lymph nodes: opportunities, challenges, and future directions in colorectal cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jan 19;12(1):e008026. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008026. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38242718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sprenger T, Rothe H, Conradi LC, et al. Stage-dependent frequency of lymph node metastases in patients with rectal carcinoma after preoperative chemoradiation: results from the CAO/ARO/AIO-94 trial and from a comparative prospective evaluation with extensive pathological workup. Dis Colon Rectum. 2016;59(5):377–385. doi:10.1097/DCR.0000000000000570 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous