Raltitrexed Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Apatinib in Human Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cells via Akt and Erk Pathways
- PMID: 33293826
- PMCID: PMC7719348
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S276125
Raltitrexed Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Apatinib in Human Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cells via Akt and Erk Pathways
Abstract
Objective: Apatinib has been proved effective in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer and a variety of solid tumors. Raltitrexed is emerging as a promising alternative for treating advanced colorectal cancer in China. This work aims to study the combinatory antitumor effect of apatinib and raltitrexed on human esophageal squamous carcinoma cells (ESCC).
Materials and methods: Two VEGFR-2-positive human ESCC lines, KYSE-30 and TE-1, were treated with apatinib or raltitrexed, or both, then the cell proliferation rate was measured by MTS assay; cell migration and invasion were studied by transwell assays; cell apoptosis rate was determined by flow cytometry; cellular autophagy level affected was analyzed by Western blot analysis; finally, quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was used to monitor transcription and Western blot was performed to check phosphorylation of apoptotic proteins after treatment.
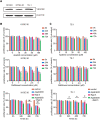
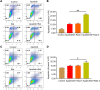
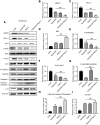
Results: Both apatinib and raltitrexed significantly inhibited KYSE-30 and TE-1 cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with both drugs showed enhanced inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasiveness compared with apatinib monotherapy. Apoptosis percentages in both cell lines were also remarkably increased by the combined treatment. Moreover, the combination of apatinib and raltitrexed down-regulated mRNA level of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, while up-regulated pro-apoptotic protein PARP, Bax, and caspase-3 transcription. Western blot analysis showed that phosphorylation levels of Erk, Akt, and invasiveness-associated protein matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9) were decreased in the combination group.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results indicate that raltitrexed enhances the antitumor effects of apatinib on human ESCC cells by down-regulating phosphorylation of Akt and Erk, implying a combination of raltitrexed and apatinib might be an effective option for treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Keywords: Akt; ESCC; Erk; antitumor; apatinib; raltitrexed.
© 2020 Zhen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Raltitrexed enhanced antitumor effect of anlotinib in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cells on proliferation, invasiveness, and apoptosis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Mar 4;23(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10691-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36870981 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine Astragalus polysaccharide enhanced antitumor effects of the angiogenesis inhibitor apatinib in pancreatic cancer cells on proliferation, invasiveness, and apoptosis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 May 9;11:2685-2698. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S157129. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29785118 Free PMC article.
-
[The inhibition effects of apatinib on cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in esophageal carcinoma via Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and JAK2/STAT3 pathways].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 23;41(4):263-275. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.04.005. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31014051 Chinese.
-
Apatinib induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and autophagy and potentiates cell sensitivity to paclitaxel via the IRE-1α-AKT-mTOR pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Biosci. 2021 Jul 6;11(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00640-2. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34229754 Free PMC article.
-
The coordinated effects of Apatinib and Tripterine on the proliferation, invasiveness and apoptosis of human hepatoma Hep3B cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):353-361. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8656. Epub 2018 May 7. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29928421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blocking STAT3 signaling augments MEK/ERK inhibitor efficacy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 May 25;13(5):496. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04941-3. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35614034 Free PMC article.
-
Raltitrexed enhanced antitumor effect of anlotinib in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cells on proliferation, invasiveness, and apoptosis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Mar 4;23(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10691-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36870981 Free PMC article.
-
Computational drug repurposing of Akt-1 allosteric inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 May 16;13(1):7947. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35122-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37193898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieto E, Ferraraccio F, Orditura M, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an independent prognostic indicator of worse outcome in gastric cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(1):69–79. doi:10.1245/s10434-007-9596-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

