Genomic analysis reveals neutral and adaptive patterns that challenge the current management regime for East Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L
- PMID: 33294016
- PMCID: PMC7691467
- DOI: 10.1111/eva.13070
Genomic analysis reveals neutral and adaptive patterns that challenge the current management regime for East Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L
Abstract
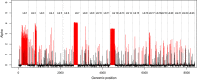
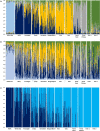
Challenging long-held perceptions of fish management units can help to protect vulnerable stocks. When a fishery consisting of multiple genetic stocks is managed as a single unit, overexploitation and depletion of minor genetic units can occur. Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) is an economically and ecologically important marine species across the North Atlantic. The application of new genomic resources, including SNP arrays, allows us to detect and explore novel structure within specific cod management units. In Norwegian waters, coastal cod (i.e. those not undertaking extensive migrations) are divided into two arbitrary management units defined by ICES: one between 62° and 70°N (Norwegian coastal cod; NCC) and one between 58° and 62°N (Norwegian coastal south; NCS). Together, these capture a fishery area of >25,000 km2 containing many spawning grounds. To assess whether these geographic units correctly represent genetic stocks, we analysed spawning cod of NCC and NCS for more than 8,000 SNPs along with samples of Russian White Sea cod, north-east Arctic cod (NEAC: the largest Atlantic stock), and outgroup samples representing the Irish and Faroe Sea's. Our analyses revealed large differences in spatial patterns of genetic differentiation across the genome and revealed a complex biological structure within NCC and NCS. Haplotype maps from four chromosome sets show regional specific SNP indicating a complex genetic structure. The current management plan dividing the coastal cod into only two management units does not accurately reflect the genetic units and needs to be revised. Coastal cod in Norway, while highly heterogenous, is also genetically distinct from neighbouring stocks in the north (NEAC), west (Faroe Island) and the south. The White Sea cod are highly divergent from other cod, possibly yielding support to the earlier notion of subspecies rank.
Keywords: White Sea cod; chromosomes; haplotype maps; inversions; managements.
© 2020 The Authors. Evolutionary Applications published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Becker, R. A. , & Wilks, R. A. (2018). R‐package maps: Draw Geographical Maps. Retrieved from https://CRAN.R-project/package=maps
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

