Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia
- PMID: 33294118
- PMCID: PMC7690998
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2963540
Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia
Abstract
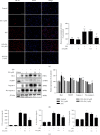
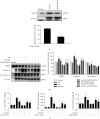
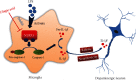
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the pathological process of Parkinson's disease (PD). Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome was highly located in microglia and involved in the process of neuroinflammation. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome has been confirmed to contribute to the progression of PD. Thus, inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation could be an important breakthrough point on PD therapy. Ellagic acid (EA) is a natural polyphenol that has been widely found in soft fruits, nuts, and other plant tissues with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. However, the mechanisms underlying EA-mediated anti-inflammation and neuroprotection have not been fully elucidated. In this study, a lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced rat dopamine (DA) neuronal damage model was performed to determine the effects of EA on the protection of DA neurons. In addition, the DA neuronal MN9D cell line and microglial BV-2 cell line were employed to explore whether EA-mediated neuroprotection was through an NLRP3-dependent mechanism. Results indicated that EA ameliorated LPS-induced DA neuronal loss in the rat substantia nigra. Further, inhibition of microglial NLRP3 inflammasome signaling activation was involved in EA-generated neuroprotection, as evidenced by the following observations. First, EA reduced NLRP3 inflammasome signaling activation in microglia and subsequent proinflammatory cytokines' excretion. Second, EA-mediated antineuroinflammation and further DA neuroprotection from LPS-induced neurotoxicity were not shown upon microglial NLRP3 siRNA treatment. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that EA has a profound effect on protecting DA neurons against LPS-induced neurotoxicity via the suppression of microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Copyright © 2020 Xue-mei He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Naringenin Produces Neuroprotection Against LPS-Induced Dopamine Neurotoxicity via the Inhibition of Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Front Immunol. 2019 May 1;10:936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00936. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31118933 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacoside protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease model.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Nov;164:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.015. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32846198
-
Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease model.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Apr 1;207:108963. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.108963. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35065082
-
Targeting Microglial α-Synuclein/TLRs/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis in Parkinson's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:719807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719807. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2020 Jan;35(1):20-33. doi: 10.1002/mds.27874. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 31680318 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Flavonoids and Flavonoid Metabolites in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Pathology in Disorders of Cognitive Decline.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;12(3):663. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030663. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of NLRP3 in Parkinson's disease: Specific activation especially in dopaminergic neurons.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 28;10(7):e28838. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28838. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plants' Impact on the Human Brain-Exploring the Neuroprotective and Neurotoxic Potential of Plants.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 7;17(10):1339. doi: 10.3390/ph17101339. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasomes as therapeutic targets in human diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jul 2;6(1):247. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00650-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34210954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic plasticity and cognitive impairment consequences to acute kidney injury: Protective role of ellagic acid.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 May;25(5):621-628. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.62015.13729. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35911650 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

