Neglected extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis patients with normal body mass index: reduced skeletal muscle overlapping overfat
- PMID: 33294150
- PMCID: PMC7705189
- DOI: 10.1177/2040622320975241
Neglected extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis patients with normal body mass index: reduced skeletal muscle overlapping overfat
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can induce reduced muscle mass (myopenia) and ectopic fat deposition probably showing normal body mass index (BMI). We aimed to investigate their body composition (BC) characteristics and clinical significance.
Methods: BMI and BC were collected in consecutive RA patients and control subjects. Myopenia was defined by appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) ⩽7.0 kg/m2 in men and ⩽5.7 kg/m2 in women. Overfat was defined by body fat percentage (BF%) as ⩾25% for men and ⩾35% for women.
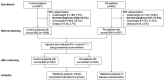
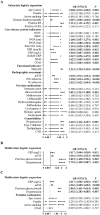
Results: There were 620 RA patients (57.6% with normal BMI) and 2537 control subjects (62.5% with normal BMI) recruited. After 1:1 age and sex matching with control subjects, RA patients with normal BMI (n = 240) showed significantly higher prevalence of myopenia (43.3% versus 22.1%) and overfat (19.2% versus 7.1%) as well as myopenia overlapping overfat (17.1% versus 3.3%). In all RA patients with normal BMI (n = 357), there were 18.2% patients with myopenia overlapping overfat who had the worst radiographic scores and highest rates of previous glucocorticoid treatment and hypertension. Compared with those without, normal BMI RA patients with previous glucocorticoid treatment (24.4% versus 10.3%) or hypertension (27.8% versus 13.6%) had a higher rate of myopenia overlapping overfat. Previous glucocorticoid treatment [odds ratio (OR) = 2.844, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.441-5.614] and hypertension (OR = 2.452, 95% CI 1.283-4.685) were potential associated factors of myopenia overlapping overfat in RA patients with normal BMI.
Conclusion: Myopenia overlapping overfat is an important extra-articular manifestation which should not be ignored in RA patients with normal BMI, especially with glucocorticoid treatment and hypertension.
Keywords: body composition; body fat; body mass index; hypertension; rheumatoid arthritis; skeletal muscle.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 2018; 320: 1360–1372. - PubMed
-
- Salaffi F, Di Carlo M, Farah S, et al. Prevalence of frailty and its associated factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional analysis. Clin Rheumatol 2019; 38: 1823–1830. - PubMed
-
- Salaffi F, Di Carlo M, Farah S, et al. The comprehensive rheumatologic assessment of frailty (CRAF): development and validation of a multidimensional frailty screening tool in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2020; 38: 488–499. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

