Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Pneumocystis Pneumonia of an Infant with AIDS
- PMID: 33294246
- PMCID: PMC7688365
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8840131
Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Pneumocystis Pneumonia of an Infant with AIDS
Abstract
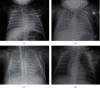
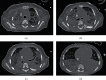
Pneumocystis pneumonia is a common complication of cellular immunosuppression and may trigger severe pulmonary complications. Rapid onset of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is possible in infants infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). We report here the case of a 13-week-old girl who was previously healthy presenting with altered immunity and refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) initially attributed to bacterial pneumonia. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) was initiated because her condition was poor. An HIV infection was later fortuitously diagnosed after accidental exposure of a nurse to the child's urine. The mother had congenitally transmitted HIV to the child after late (undetected) infection during pregnancy. The lung lesions were finally attributed to Pneumocystis pneumonia. We prescribed combined antiretroviral, antibiotic, and steroid therapy aimed at preventing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. VV-ECMO weaning progressed over 30 days to the time of decannulation, rapidly followed by extubation and hospital discharge. The case highlights the fact that rare curable causes of refractory pediatric ARDS should always be investigated early. VV-ECMO should not be excluded as an ARDS treatment for immunocompromised children.
Copyright © 2020 Grégoire Cane et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment in an Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Patient with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Complicating Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia: A Challenging Case.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Feb 26;21:e919570. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.919570. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32098943 Free PMC article.
-
The use of ECMO in HIV/AIDS with Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia: a case report and review of the literature.ASAIO J. 2014 Sep-Oct;60(5):606-8. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000112. ASAIO J. 2014. PMID: 25166733 Review.
-
Early application of awake extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia complicated with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 19;10:1264928. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1264928. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37928461 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a 29-Year-Old Man with Pneumocystis jirovecii Respiratory Failure and AIDS.Tex Heart Inst J. 2018 Aug 1;45(4):254-259. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-16-6186. eCollection 2018 Aug. Tex Heart Inst J. 2018. PMID: 30374241 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory, life-threatening, and herpes simplex virus 1-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Our experience and literature review.Am J Emerg Med. 2012 Jul;30(6):1014.e3-1014.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Am J Emerg Med. 2012. PMID: 21665410 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the treatment of critical Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in a child with Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 9;25(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10893-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40205543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali H. S., Hassan I. F., George S. Extra corporeal membrane oxygenation to facilitate lung protective ventilation and prevent ventilator-induced lung injury in severe Pneumocystis pneumonia with pneumomediastinum: a case report and short literature review. BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 2016;16(1):p. 52. doi: 10.1186/s12890-016-0214-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

