Synovial Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived EV-Packaged miR-31 Downregulates Histone Demethylase KDM2A to Prevent Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 33294294
- PMCID: PMC7691165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.014
Synovial Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived EV-Packaged miR-31 Downregulates Histone Demethylase KDM2A to Prevent Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
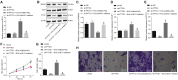
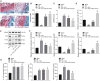
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as important mediators of intercellular communication in response to cartilage damage. In this study, we sought to characterize the inhibitory role of microRNA (miR)-31 encapsulated in synovial MSC (SMSC)-derived EVs in knee osteoarthritis (OA). The expression of miR-31, lysine demethylase 2A (KDM2A), E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1), and pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 (PTTG1) was validated in cartilage tissues of knee OA patients. Following SMSC-EV extraction and identification, chondrocytes with the miR-31 inhibitor were added with SMSC-EVs, whereupon the effects of miR-31 on proliferation and migration of chondrocytes were assessed. The interaction among miR-31, KDM2A, E2F1, and PTTG1 in chondrocyte activities was probed in vitro, along with an in vivo mouse knee OA model. We identified downregulated miR-31, E2F1, and PTTG1 and upregulated KDM2A in cartilage tissues of knee OA patients. SMSC-EV-packaged miR-31 potentiated chondrocyte proliferation and migration as well as cartilage formation by targeting KDM2A. Mechanistically, KDM2A bound to the transcription factor E2F1 and inhibited its transcriptional activity. Enrichment of E2F1 in the PTTG1 promoter region activated PTTG1 transcription, accelerating chondrocyte proliferation and migration. SMSC-EVs and EVs from miR-31-overexpressed SMSCs alleviated cartilage damage and inflammation in knee joints in vivo. SMSC-EV-encapsulated miR-31 ameliorates knee OA via the KDM2A/E2F1/PTTG1 axis.
Keywords: E2F1; KDM2A; PTTG1; knee osteoarthritis; mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles; microRNA-31.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRN555A-26a-5p ameliorate cartilage damage of osteoarthritis.J Gene Med. 2021 Nov;23(11):e3379. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3379. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Gene Med. 2021. PMID: 34296780
-
Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model.Theranostics. 2017 Jan 1;7(1):180-195. doi: 10.7150/thno.17133. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28042326 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate chondrocyte damage during osteoarthritis through microRNA-130b-3p-mediated inhibition of the LRP12/AKT/β-catenin axis.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022 Apr;44(2):247-260. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2038192. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022. PMID: 35174753
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Potential Significance in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 1;14(4):315. doi: 10.3390/ph14040315. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33915903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-bound extracellular vesicle as novel therapy for osteoarthritis.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2022 Jun 1;12(2):1-9. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1308. eCollection 2022. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2022. PMID: 35836973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-31 from Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting NFAT5 and Upregulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Oct 20;2022:2164057. doi: 10.1155/2022/2164057. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 36311041 Free PMC article.
-
Breakthrough of extracellular vesicles in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis.Bioact Mater. 2022 Oct 20;22:423-452. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.012. eCollection 2023 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 36311050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for cell-free therapy of ocular diseases.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2022 Apr 24;3(2):102-117. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2022.08. eCollection 2022. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2022. PMID: 39698446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone demethylases in autophagy and inflammation.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-02006-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39806430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Treatments for Osteoarthritis.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 25;15(7):1814. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071814. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li H., Guo H., Lei C., Liu L., Xu L., Feng Y., Ke J., Fang W., Song H., Xu C. Nanotherapy in Joints: Increasing Endogenous Hyaluronan Production by Delivering Hyaluronan Synthase 2. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:e1904535. - PubMed
-
- Hunter D.J., Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393:1745–1759. - PubMed
-
- Hosseinzadeh A., Kamrava S.K., Joghataei M.T., Darabi R., Shakeri-Zadeh A., Shahriari M., Reiter R.J., Ghaznavi H., Mehrzadi S. Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2016;61:411–425. - PubMed
-
- Mirzaei H., Sahebkar A., Sichani L.S., Moridikia A., Nazari S., Sadri Nahand J., Salehi H., Stenvang J., Masoudifar A., Mirzaei H.R., Jaafari M.R. Therapeutic application of multipotent stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018;233:2815–2823. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

