Are losartan and imatinib effective against SARS-CoV2 pathogenesis? A pathophysiologic-based in silico study
- PMID: 33294307
- PMCID: PMC7716628
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-020-00058-7
Are losartan and imatinib effective against SARS-CoV2 pathogenesis? A pathophysiologic-based in silico study
Abstract
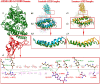
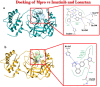
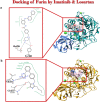
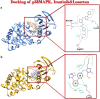
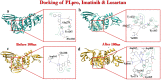
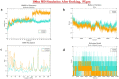
Proposing a theory about the pathophysiology of cytokine storm in COVID19, we were to find the potential drugs to treat this disease and to find any effect of these drugs on the virus infectivity through an in silico study. COVID-19-induced ARDS is linked to a cytokine storm phenomenon not explainable solely by the virus infectivity. Knowing that ACE2, the hydrolyzing enzyme of AngII and SARS-CoV2 receptor, downregulates when the virus enters the host cells, we hypothesize that hyperacute AngII upregulation is the eliciting factor of this ARDS. We were to validate this theory through reviewing previous studies to figure out the role of overzealous activation of AT1R in ARDS. According to this theory losartan may attenuate ARDS in this disease. Imatinib, has previously been elucidated to be promising in modulating lung inflammatory reactions and virus infectivity in SARS and MERS. We did an in silico study to uncover any probable other unconsidered inhibitory effects of losartan and imatinib against SARS-CoV2 pathogenesis. Reviewing the literature, we could find that over-activation of AT1R could explain precisely the mechanism of cytokine storm in COVID19. Our in silico study revealed that losartan and imatinib could probably: (1) decline SARS-CoV2 affinity to ACE2. (2) inhibit the main protease and furin, (3) disturb papain-like protease and p38MAPK functions. Our reviewing on renin-angiotensin system showed that overzealous activation of AT1R by hyper-acute excess of AngII due to acute downregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV2 explains precisely the mechanism of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Besides, based on our in silico study we concluded that losartan and imatinib are promising in COVID19.
Keywords: Cytokine storm; Imatinib; Losartan; Main protease; Papain-like protease; SARS-CoV2.
© Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akashi N, Matsumoto I, Tanaka Y, Inoue A, Yamamoto K, Umeda N, Tanaka Y, Hayashi T, Goto D, Ito S. Comparative suppressive effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib in models of autoimmune arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21(3):267–275. doi: 10.3109/s10165-010-0392-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Appel S, Rupf A, Weck MM, Schoor O, Brümmendorf TH, Weinschenk T, Grünebach F, Brossart P. Effects of imatinib on monocyte-derived dendritic cells are mediated by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and Akt signaling pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(5):1928–1940. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1713. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arendse LB, Danser AJ, Poglitsch M, Touyz RM, Burnett JC, Llorens-Cortes C, Ehlers MR, Sturrock ED. Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure. Pharmacol Rev. 2019;71(4):539–570. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.017129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

