Stem cells: a new way of therapy for cardiovascular disorders
- PMID: 33294428
- PMCID: PMC7715658
- DOI: 10.21037/sci-2019-048
Stem cells: a new way of therapy for cardiovascular disorders
Abstract
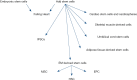
Cardiovascular disorder affects the overall health of an individual and hence the quality of life. Stem cell therapy involves the use of stem cells widely used to treat different conditions. People having severe cardiovascular disorder can be treated with stem cells by generating heart muscles, stimulating the growth of blood vessels and by the secretion of different growth factors. Different types of stem cells are used for cardiac repair. Adipose stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells are better options for increasing the survival rate. In this review we will discuss different types of stem cells, their activation pathway, generation, hurdles in transplantation and how to overcome them and their applications.
Keywords: ASC’s; Cardiovascular disorders; cardiac dysfunction; induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSC’s); viability.
2020 Stem Cell Investigation. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/sci-2019-048). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
