Data for the cytotoxicity, self-assembling properties and synthesis of 4-pyridinium-1,4-dihydropyridines
- PMID: 33294531
- PMCID: PMC7701313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106545
Data for the cytotoxicity, self-assembling properties and synthesis of 4-pyridinium-1,4-dihydropyridines
Abstract
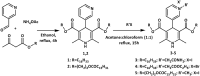
In this data file the synthetic procedures for preparation of the original 4-pyridinium-1,4-dihydropyridines (4-Py-1,4-DHP) and their parent compounds - dialkyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-pyridyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylates were described. In total, 5 unpublished compounds were obtained and characterised. All the structures of original compounds were confirmed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR, including 1H NMR and 13C NMR) and low resolution mass spectra (MS) data. Additionally, the cytotoxic properties of four 4-Py-1,4-DHPs were evaluated on 3 cell lines - normal NIH3T3 (mouse embryonic fibroblast), cancerous HT-1080 (human lung fibrosarcoma) and MH-22A (mouse hepatoma) and self-assembling properties were studied and characterisation of formed nanoparticles were performed using dynamic light scattering technique. In this article provided data are directly related to the previously published research articles - "Novel cationic amphiphilic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives for DNA delivery" [1] where compound 5 was tested as gene delivery agent without full physico-chemical characterisation and "Synthesis and studies of calcium channel blocking and antioxidant activities of novel 4-pyridinium and/or N-propargyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives" [2] where synthesis and physico-chemical characterisation as well as calcium channel blocking and antioxidant activities were described for compound 6. Synthesis of other compounds - parent 1,4-DHPs 1 and 2, and 4-Py-1,4-DHPs 3-5, their characterisation, estimation of cytotoxicity and self-assembling properties for all 4-Py-1,4-DHPs 3-6 are reported herein for the first time. Information provided in this data file can be used in medicinal chemistry by other scientists to estimate structure-activity relationships for the analysis and construction of various cationic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives and related heterocycles.
Keywords: 1,4-dihydropyridine; Cytotoxicity; Nanoparticles; Pyridinium; Quaternisation; Self-assembling; Structure-activity relationships.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Hyvonen Z., Plotniece A., Reine I., Chekavichus B., Duburs G., Urtti A. Novel cationic amphiphilic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives for DNA delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1509(1–2):451–466. - PubMed
-
- Rucins M., Kaldre D., Pajuste K., Fernandes M.A.S., Vicente J.A.F., Klimaviciusa L., Jaschenko E., Kanepe-Lapsa I., Shestakova I., Plotniece M., Gosteva M., Sobolev A., Jansone B., Muceniece R., Klusa V., Plotniece A. Synthesis and studies of calcium channel blocking and antioxidant activities of novel 4-pyridinium and/or N-propargyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives. C. R. Chim. 2014;17(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2013.07.003. - DOI
-
- Fox H.H., Lewis J.I., Wenner W. Derivatives of 1,3-Dimethyl-2-Azafluorene (1,3-Dimethyl-9-Indeno[2,1-c]Pyridine) J. Org. Chem. 1951;16(8):1259–1270. doi: 10.1021/jo50002a012. - DOI
-
- Meekel A.A.P., Wagenaar A., Šmisterová J., Kroeze J.E., Haadsma P., Bosgraaf B., Stuart M.C.A., Brisson A., Ruiters M.H.J., Hoekstra D., Engberts J.B.F.N. Synthesis of pyridinium amphiphiles used for transfection and some characteristics of Amphiphile/DNA complex formation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000;2000(4):665–673. 10.1002/(sici)1099-0690(200002)2000:4<665::aid−ejoc665>3.0.co;2-a.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources