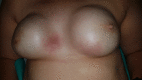
Reticular telangiectatic erythema by breast implants
- PMID: 33294578
- PMCID: PMC7695883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2020.10.006
Reticular telangiectatic erythema by breast implants
Abstract
Reticular telangiectatic erythema is a benign dermatosis which has been described on patients with pacemakers, implantable devices or materials inserted in their body. Etiology of this entity hasn't been clarified since the first description in 1981 but it is suggested that physical or mechanical factors have to be involved. We present the second case of bilateral reticular telangiectatic erythema by breast implants described in the literature.
Keywords: Breast implants; Implantable device; Pacemaker; Post-implantation erythema; Reticular erythema; Reticular telangiectatic erythema.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Gensch E.G., Schmitt C.G. Circumscribed reticular telangiectatic erythema following implantation of a heart pacemaker. Hautarzt. 1981;32:651–654. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources