Perforating foreign body causing incomplete facial paralysis
- PMID: 33294580
- PMCID: PMC7689329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2020.100370
Perforating foreign body causing incomplete facial paralysis
Abstract
Facial nerve trauma is a common cause of facial paralysis; both blunt and penetrating forces may compromise the facial nerve. A comprehensive primary and secondary survey is essential for diagnosis and treatment of the injury. Here we report on a young patient who sustained a quad bike accident, leading to an perforating injuries of the face from a bough, causing facial paralysis.
Keywords: Facial muscle weakness; Facial nerve trauma; Facial paralysis; Foreign body; Perforating injuries; Traumatic facial paralysis.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods referred in this case report or the findings specified in this article. The authors state that this work has not been previously published in whole or in part or submitted elsewhere for review.
Figures


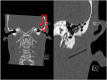
References
-
- Lee L.N., Lyford-Pike S., Boahene K.D. Traumatic facial nerve injury. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2013;46(5):825–839. - PubMed
-
- Greywoode J.D. Management of traumatic facial nerve injuries. Facial Plast. Surg. 2010;26(6):511–518. - PubMed
-
- Hadlock T. Facial paralysis: research and future directions. Facial Plast. Surg. 2008;24(2):260–267. - PubMed
-
- Chu E.A., Byrne P.J. Treatment considerations in facial paralysis. Facial Plast. Surg. 2008;24(2):164–169. - PubMed
-
- Conley J., Baker D.C. Hypoglossal-facial nerve anastomosis for reinnervation of the paralyzed face. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1979;63(1):63–72. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

