Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) and molecular docking of xanthone derivatives as anti-tuberculosis agents
- PMID: 33294629
- PMCID: PMC7695880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2020.100203
Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) and molecular docking of xanthone derivatives as anti-tuberculosis agents
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2021 May 6;24:100242. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2021.100242. eCollection 2021 Aug. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2021. PMID: 34095548 Free PMC article.
Abstract
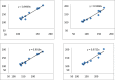
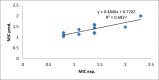
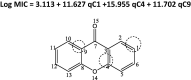
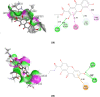
Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) and molecular docking approach were carried out to design novel anti-tuberculosis agents based on xanthone derivatives. QSAR designed new compounds were calculated by Austin Model 1 (AM1) methods and analysis of multi-linear regression (MLR). The result showed that the best model as follows: Log IC50 = 3.113 + 11.627 qC1 + 15.955 qC4 + 11.702 qC9, this result has appropriate some statistical parameters (PRESS = 2.11, r2 = 0.730, SEE = 0. 3545, R = 0.6827, FCal/FTab = 4.68), and being used to design a potential anti-tuberculosis drugs with substituted amide, sulfoxide, and carboxylate group xanthone scaffold by a number of their inhibitory concentration (IC50). The mechanism action of sulfonamide substituted on the xanthone scaffold as anti-tuberculosis was carried out using molecular docking. Docking inhibition studies were carried out on MTB C171Q receptor (4C6X.pdb) as KasA inhibitors using by the discovery studio. Based on the binding interaction showed, the sulfonamide substituted xanthone has potential being the anti-tuberculosis drugs by KasA inhibitor for target drug activity.
Keywords: Anti-tuberculosis; Docking; QSAR; Xanthone; kasA inhibitor.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis report, 2018.
-
- Dey R., Nandi S., Samadder A., Saxena A., Saxena A.K. Exploring new tuberculosis drug targets and structure-based design of their potential inhibitors for clinical investigation. Curr Topics Med Chemn. 2020
-
- Tripathi R.P., Tewari N., Dwivedi N., Tiwari V.K. Fighting tuberculosis: an old disease with new challenges. Med Res Rev. 2005;25:93–131. - PubMed
-
- Alcalde E., Dinares I., Frigola J. NMR studies of N-(benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridinium derivatives: QSAR with the anti-leishmanial activity and their carbon-13 NMR chemical shiftsÉtude RMN de dérivés N-(benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridinium: établissement du QSAR entre l'activité antileishmania et les déplacements chimiques en 13C RMN. Eur J Med Chem. 1991;26:633–642.
-
- Guha R., Jurs P.C. 2004, Development of QSAR Models To Predict and Interpret the Biological Activity of Artemisinin Analogues. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004;44(4):1440–1449. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

