Developing Human Skin Contains Lymphocytes Demonstrating a Memory Signature
- PMID: 33294857
- PMCID: PMC7691438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100132
Developing Human Skin Contains Lymphocytes Demonstrating a Memory Signature
Abstract
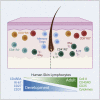
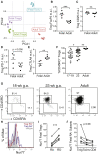
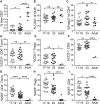
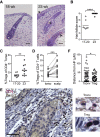
Lymphocytes in barrier tissues play critical roles in host defense and homeostasis. These cells take up residence in tissues during defined developmental windows, when they may demonstrate distinct phenotypes and functions. Here, we utilized mass and flow cytometry to elucidate early features of human skin immunity. Although most conventional αβ T (Tconv) cells in fetal skin have a naive, proliferative phenotype, a subset of CD4+ Tconv and CD8+ cells demonstrate memory-like features and a propensity for interferon (IFN)γ production. Skin regulatory T cells dynamically accumulate over the second trimester in temporal and regional association with hair follicle development. These fetal skin regulatory T cells (Tregs) demonstrate an effector memory phenotype while differing from their adult counterparts in expression of key effector molecules. Thus, we identify features of prenatal skin lymphocytes that may have key implications for understanding antigen and allergen encounters in utero and in infancy.
Keywords: Tregs; fetal; hair follicle development; human skin; lymphocytes; memory T cells; skin development.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.R. is a founder and consultant for TRex Bio and Sitryx Bio and receives research funding from Abbvie, TRex, and LEO Pharma. K.T. is currently an employee of Amgen. E.G.L. is currently an employee of SentiBio. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Clark R.A., Chong B., Mirchandani N., Brinster N.K., Yamanaka K.-I., Dowgiert R.K., Kupper T.S. The vast majority of CLA+ T cells are resident in normal skin. J. Immunol. 2006;176:4431–4439. - PubMed
-
- Hoath S.B., Maibach H.I. CRC Press; 2003. Neonatal Skin: Struture and Function.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

