Impact of 2020 SARS-CoV-2 outbreak on telemedicine management of cardiovascular disease in Italy
- PMID: 33294959
- PMCID: PMC7722980
- DOI: 10.1007/s11739-020-02564-0
Impact of 2020 SARS-CoV-2 outbreak on telemedicine management of cardiovascular disease in Italy
Abstract
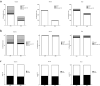
The Covid-19 pandemic affected large part of Italy since February 2020; we, therefore, aimed to assess the impact of 2020 SARS-CoV-2 outbreak on telemedicine management of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in Italy. We analyzed data from three telemedicine dispatch centers, one located in Genoa, serving private clients (pharmacies, general practitioners), one in Brescia, serving pharmacies, and one in Bari, serving regional public STEMI network and emergency medical service in Apulia (4 million inhabitants). Demographic data and principal electrocardiogram diagnosis were collected and analyzed. Records from the time interval March 1, 2020 and April 1, 2020 were compared with the corresponding period in 2019. The comparative analysis of data shows a 54% reduction of telemedicine electrocardiogram transmission in Genoa telemedicine center (from 364 to 166), 68% in Brescia (from 5.745 to 1.905), 24% in Bari (from 15.825 to 11.716); relative reduction according to electrocardiogram diagnosis was 38% for acute coronary syndrome, 40% for other acute CVD in Genoa center, 24% for acute coronary syndrome, and 38% for other acute CVD in Bari. Male/female ratio remained substantially unchanged. A dramatic reduction of telemedicine access for CVD was observed during Covid-19 outbreak in March 2020 in Italy. The reduction was substantially consistent for all electrocardiogram findings, ACS, other acute CVD and normal.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Covid-19; Telemedicine.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Telemedicine and the risk of overshadowing children with Kawasaki disease in a worldwide coronavirus pandemic climate.Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Oct;16(7):2027-2028. doi: 10.1007/s11739-021-02662-7. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33582891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU)". ArcGIS. Johns Hopkins CSSE. https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
-
- https://www.tctmd.com/news/mystery-missing-stemis-during-covid-19-pandemic. Accessed on April 10 2020.
-
- Brunetti ND, Molinari G, Acquistapace F, Zimotti T, Parati G, Indolfi C, Fedele F, Carugo S. 2019 italian society of cardiology census on telemedicine in cardiovascular disease: a report from the working group on telecardiology and informatics. Open Heart. 2020;7:e001157. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2019-001157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caldarola P, Gulizia MM, Gabrielli D, Sicuro M, De Gennaro L, Giammaria M, Grieco NB, Grosseto D, Mantovan R, Mazzanti M, Menotti A, Brunett ND, Severi S, Russo G, Gensini GF. ANMCO/SIT consensus document: telemedicine for cardiovascular emergency networks. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2017;19:D229–D243. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/sux028. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

