Effect of Multiple Doses of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid on Perioperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Study
- PMID: 33295133
- PMCID: PMC7862185
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12850
Effect of Multiple Doses of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid on Perioperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
Objective: To identify the efficacy and safety of multiple doses of intravenous tranexamic acid (IV-TXA) following primary total knee arthroplasty (TKA) with a tourniquet.
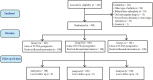
Methods: This is a single-blind randomized controlled study that recruited osteoarthritis patients who had undergone primary unilateral TKA from May 2019 to May 2020 at our medical center. A total of 300 patients were randomly divided into three groups to receive: one dose (1 g) of IV-TXA before skin incision combined with one dose (1.5 g) of intra-articular tranexamic acid(IA-TXA) followed by a single dose of IV-TXA (1 g) for 3 h (group A); two doses of IV-TXA (1 g) for 3 and 6 h (group B); or three doses of IV-TXA (1 g) for 3, 6, and 12 h (group C) postoperatively. TKA with a tourniquet was performed by the same surgical team. The primary outcomes were total blood cell loss (TBL), hidden blood loss (HBL), maximum hemoglobin (Hb) drop, and transfusion rate. Secondary outcomes were levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and D-dimer, and the incidence of postoperative complications. One-way analysis of variance, subgroup analysis, and multivariate correlation analysis were used to calculate the differences among the three groups.
Results: The study included 56 male and 244 female patients aged 60-80 years. The mean TBL, the mean HBL, and the maximum Hb drop in group C (471.2 ± 190.6 mL, 428.4 ± 190.3 mL, and 21.2 ± 3.8 g/L, respectively) were significantly lower than those in groups B (563.4 ± 224.6 mL, P = 0.030; 519.9 ± 226.4 mL, P = 0.033; and 23.2 ± 4.1 g/L, P = 0.001, respectively), and A (651.6 ± 254.1 mL, P < 0.001; 607.1 ± 254.3 mL, P < 0.001; and 25.1 ± 4.3 g/L, P < 0.001, respectively). No transfusions were required. The postoperative acute inflammatory reaction was less problematic for patients in Group C, and the incidence of thromboembolic events was similar among the groups (P > 0.05). In addition, there were positive correlations between the HBL and the tourniquet inflation time (r = 0.844, P < 0.001). Similarly, the level of CRP on POD1 (r = 0.393, P < 0.001) and POD3 (r = 0.149, P = 0.010), and the level of D-dimer on POD1 (r = 0.382, P < 0.001) were positively correlated with the HBL.
Conclusion: Three doses of postoperative IV-TXA decreased blood loss and diminished the postoperative inflammatory and fibrinolytic response more than a single dose or two doses in elderly patients following TKA without increasing the incidence of adverse events.
Keywords: Osteoarthritis of the knee; Surgical blood loss; Total knee arthroplasty; Tranexamic acid.
© 2020 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Chinese Orthopaedic Association and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2007, 89: 780–785. - PubMed
-
- Freedman J, Luke K, Escobar M, Vernich L, Chiavetta JA. Experience of a network of transfusion coordinators for blood conservation (Ontario transfusion coordinators [ONTraC]). Transfusion, 2008, 48: 237–250. - PubMed
-
- Schnettler T, Papillon N, Ree H. Use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty causes a paradoxical increase in total blood loss. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2017, 99: 1331–1336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous