Crocin inhibits the activation of mouse hepatic stellate cells via the lnc-LFAR1/MTF-1/GDNF pathway
- PMID: 33295246
- PMCID: PMC7781632
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1848064
Crocin inhibits the activation of mouse hepatic stellate cells via the lnc-LFAR1/MTF-1/GDNF pathway
Abstract
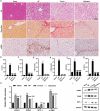
Crocin is the main monomer of saffron, which is a momentous component of traditional Chinese medicine Lang Qing A Ta. Here, we tried to probe into the role of crocin in liver fibrosis. Hematoxylin-eosin staining and Sirius Red staining were used to observe the pathological changes of liver tissues. After hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were isolated from liver tissues, lnc-LFAR1, MTF-1, GDNF, and α-SMA expressions were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence were used to detect α-SMA expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was used to analyze the binding of MTF-1 to the GDNF promoter. Moreover, the dual-luciferase reporter gene, RNA pull-down, and RNA immunoprecipitation were used to clarify the interaction between MTF-1 and GDNF, lnc-LFAR1 and MTF-1. The degree of liver fibrosis was more severe in the mice from the liver fibrosis model, while the liver fibrosis was alleviated by the injection of crocin. lnc-LFAR1, GDNF, and α-SMA were up-regulated, and MTF-1 was down-regulated in liver fibrosis tissues and cells, while these trends were reversed after the injection of crocin. Besides, lnc-LFAR1 negatively regulated MTF-1 expression, and positively regulated GDNF and α-SMA expressions, and MTF-1 was enriched in the promoter region of GDNF. Furthermore, the cellular direct interactions between MTF-1 and GDNF, lnc-LFAR1 and MTF-1 were verified. In vivo experiments confirmed the relief of crocin on liver fibrosis. Our research expounded that crocin restrained the activation of HSCs through the lnc-LFAR1/MTF-1/GDNF axis, thereby ameliorating liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Crocin; GDNF; MTF-1; hepatic stellate cells; lnc-LFAR1.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
