Prognostic value of BRAF/MIR-17 signature and B-Raf protein expression in patients with colorectal cancer: A pilot study
- PMID: 33296098
- PMCID: PMC7957984
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23679
Prognostic value of BRAF/MIR-17 signature and B-Raf protein expression in patients with colorectal cancer: A pilot study
Abstract
Background: Despite the recent improvement in colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment, it still has a poor prognosis with a low survival rate. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms have proved to play a substantial role in CRC tumorigenesis and progression. According to Gene Ontology and TargetScan analyses, the B-Raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) gene is one of the microRNA-17 (miR-17) targets. We aimed to explore the prognostic value of B-Raf protein and BRAF/microRNA-17 (MIR-17) gene expression signature in CRC archived samples.
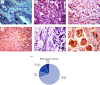
Methods: B-Raf protein expression was identified by immunohistochemistry, while gene expression studies were quantified by real-time qPCR in 53 paired archived CRC specimens.
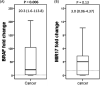
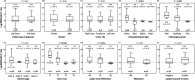
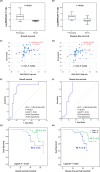
Results: The BRAF showed higher expressions in CRC specimens relative to non-cancer tissues (p = 0.006). MIR17 expression was inversely and significantly correlated with both B-Raf protein (r = -0.79, p < 0.001) and gene expression (r = -0.35, p = 0.010) and showed a significant direct correlation with a high rate of relapse (p = 0.020). BRAF/miR-17 expression in CRC was associated inversely with tumor size, high grade of colonic carcinoma, lymph node metastasis, and carcinoma subtype. Spearman correlation and Kaplan-Meier survival curve analyses revealed that disease-free survival and overall survival were inversely and significantly correlated with positive B-Raf protein expression (r = -0.31 and -0.35, p = 0.023 and 0.011, respectively) and directly correlated with log BRAF/MIR17 ratio (r = 0.50 and 0.41, p < 0.001 and = 0.003, respectively). Cox hazard regression analysis revealed the BRAF/MIR17 ratio could predict both types of patients' survival, among other variables.
Conclusion: BRAF/MIR17 ratio could have prognostic utility in patients with CRC. Further larger-scale studies are warranted to confirm this utility.
Keywords: BRAF; IHC; colorectal cancer; gene expression; miR-17; prognosis; qPCR.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relationships among KRAS mutation status, expression of RAS pathway signaling molecules, and clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 21;25(7):808-823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.808. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30809081 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations of IGF-1R and COX-2 Expressions with Ras and BRAF Genetic Mutations, Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer Patients.Pathol Oncol Res. 2018 Jan;24(1):45-57. doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0195-5. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Pathol Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28188432
-
Diagnostic Value Investigation and Bioinformatics Analysis of miR-31 in Patients with Lymph Node Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019 Dec 16;2019:9740475. doi: 10.1155/2019/9740475. eCollection 2019. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31934534 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue micro-RNAs associated with colorectal cancer prognosis: a systematic review.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Feb;48(2):1853-1867. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06075-1. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33598796
-
MicroRNA Methylome Signature and Their Functional Roles in Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Chemoresistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7281. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137281. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
USP37 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis in colorectal cancer by facilitating β-catenin stability.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;13(6):2323-2341. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37424824 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of BRAF, Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD1), and PD Ligand 1 (PDL1) Protein Expression in Colon Adenocarcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;13(2):237. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13020237. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673047 Free PMC article.
-
Association between colorectal cancer and expression levels of miR-21, miR-17-5P, miR-155 genes and the presence of Fusobacterium nucleatum in biopsy samples obtained from Iranian patients.Infect Agent Cancer. 2023 Mar 1;18(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13027-023-00494-y. Infect Agent Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36859379 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 3;23(5):2805. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052805. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 12;12(4):569. doi: 10.3390/biom12040569. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keum N, Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors, and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16(12):713‐732. - PubMed
-
- Zoratto F, Rossi L, Verrico M, et al. Focus on genetic and epigenetic events of colorectal cancer pathogenesis: implications for molecular diagnosis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(7):6195‐6206. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(5):363‐385. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

