Mechanisms of small cell lung cancer metastasis
- PMID: 33296145
- PMCID: PMC7799359
- DOI: 10.15252/emmm.202013122
Mechanisms of small cell lung cancer metastasis
Abstract
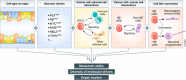
Metastasis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in cancer patients. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the ability of cancer cells to metastasize remain relatively poorly understood. Among all solid tumors, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) has remarkable metastatic proclivity, with a majority of patients diagnosed with metastatic disease. Our understanding of SCLC metastasis has been hampered for many years by the paucity of material from primary tumors and metastases, as well as the lack of faithful pre-clinical models. Here, we review recent advances that are helping circumvent these limitations. These advances include methods that employ circulating tumor cells from the blood of SCLC patients and the development of diverse genetically engineered mouse models of metastatic SCLC. New insights into the cellular mechanisms of SCLC metastasis include observations of cell fate changes associated with increased metastatic ability. Ongoing studies on cell migration and organ tropism promise to expand our understanding of SCLC metastasis. Ultimately, a better molecular understanding of metastatic phenotypes may be translated into new therapeutic options to limit metastatic spread and treat metastatic SCLC.
Keywords: NFIB; SCLC; lung cancer; metastasis; tumor heterogeneity.
© 2020 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. receives research funding from Stemcentrx/Abbvie and Pfizer, and licensed a patent to Forty Seven Inc./Gilead on the use of CD47 blocking strategies in SCLC. M.M.W. has equity in, and is an advisor for, D2G Oncology Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Aday S, Cecchelli R, Hallier‐Vanuxeem D, Dehouck MP, Ferreira L (2016) Stem cell‐based human blood‐brain barrier models for drug discovery and delivery. Trends Biotechnol 34: 382–393 - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal C, Wang X, Ranganathan A, Torigian D, Troxel A, Evans T, Cohen RB, Vaidya B, Rao C, Connelly M et al (2017) Circulating tumor cells as a predictive biomarker in patients with small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 112: 118–125 - PubMed
-
- Akoun GM, Scarna HM, Milleron BJ, Bénichou MP, Herman DP (1985) Serum neuron‐specific enolase. A marker for disease extent and response to therapy for small‐cell lung cancer. Chest 87: 39–43 - PubMed
-
- Antonia SJ, López‐Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jäger D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F et al (2016) Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small‐cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open‐label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17: 883–895 - PubMed
-
- Aupérin A, Arriagada R, Pignon J‐P, Le Péchoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, Kristjansen PEG, Johnson BE, Ueoka H, Wagner H et al (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small‐cell lung cancer in complete remission. N Engl J Med 341: 476–484 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

