Are multiple sclerosis patients and their caregivers more anxious and more committed to following the basic preventive measures during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- PMID: 33296977
- PMCID: PMC7550868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.msard.2020.102580
Are multiple sclerosis patients and their caregivers more anxious and more committed to following the basic preventive measures during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus of 2019 (COVID-19), a pandemic of the kind not seen for a century, has caused global apprehension and distress.
Objectives: to evaluate whether the psychological state and behaviours of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and their caregivers were different from the non-MS population or not during the pandemic.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted on 115 MS patients, 33 MS caregivers and 129 healthy controls. Depression anxiety stress score-21 (DASS-21) was used for evaluation of their psychological state.
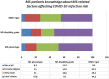
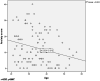
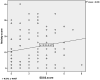
Results: MS patients had significantly higher DASS-21 scores (51.48±29.62) than their caregivers (29.79±27.19) and non-MS population (32.91±23.39) (p = 0.005). Younger patients (r=-0.252, p<0.0001), those with high EDSS scores (r = 0.023, p = 0.013) and those who believed that MS patients are at high risk for COVID-19 infection (p = 0.009) had the highest anxiety scores. There was no difference between the three groups in the level of commitment to staying at home (p = 0.747), wearing facemask (p = 0.164), wearing gloves (0.225), avoiding crowd (p = 0.225) and frequent hand washing (p = 0.570). Anxious patients had more relapses (p = 0.002) and pseudorelapses (p = 0.008).
Conclusion: In this cohort, MS patients were more anxious, stressed and depressed during the COVID-19 pandemic than their caregivers and the non-MS population, but they were not more motivated to follow the basic preventive measures against infection.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depression, anxiety, and fear of COVID-19 in patients with multiple sclerosis in pandemic era: a cross-sectional study.Neurol Sci. 2022 Jan;43(1):59-66. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05612-5. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34554334 Free PMC article.
-
The psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the general population of Saudi Arabia.Compr Psychiatry. 2020 Oct;102:152192. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2020.152192. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Compr Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32688022 Free PMC article.
-
The psychological health of patients diagnosed with cancer in Iraq during the COVID-19 pandemic: A single center study.Psychooncology. 2022 Apr;31(4):649-660. doi: 10.1002/pon.5851. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Psychooncology. 2022. PMID: 34751985 Free PMC article.
-
Fear of relapse, social support, and psychological well-being (depression, anxiety, and stress level) of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) during the COVID-19 pandemic stage.Neurol Sci. 2021 Jul;42(7):2615-2618. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05253-8. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33860396 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review.J Affect Disord. 2020 Dec 1;277:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 8. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32799105 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Possible Direct Correlation between Cognitive Impairment and Fear of Catching COVID-19 among Patients with Multiple Sclerosis.Iran J Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;16(3):336-342. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v16i3.6260. Iran J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34616468 Free PMC article.
-
Final COVID-19 Vaccination Status, Attitude, and Adverse Events Among People With Multiple Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Study From Egypt.Int J MS Care. 2025 Mar 10;27(Q1):74-81. doi: 10.7224/1537-2073.2024-057. eCollection 2025 Jan. Int J MS Care. 2025. PMID: 40071050 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on individuals living with multiple sclerosis: A rapid systematic review.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Mar;59:103562. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.103562. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35149393 Free PMC article.
-
Fear of COVID-19, problems accessing medical appointments, and subjective experience of disease progression, predict anxiety and depression reactions in patients with Multiple Sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021 Aug;53:103070. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103070. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34119745 Free PMC article.
-
The Health-Related Quality of Life Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on People Living with Multiple Sclerosis and the General Population: A Comparative Study Utilizing the EQ-5D-5L with Psychosocial Bolt-Ons.Brain Behav. 2025 Jan;15(1):e70210. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70210. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 39740771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation Report – 91 [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 21]. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- European CDC. Situation update worldwide, as of 5 April 2020 [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 16]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases.
-
- Nemati M., Ebrahimi B., Nemati F. Assessment of Iranian Nurses’ Knowledge and Anxiety Toward COVID-19 During the Current Outbreak in Iran. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 2020 In Press(In Press.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

