Heart rhythm complexity as predictors for the prognosis of end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis
- PMID: 33297978
- PMCID: PMC7727237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-020-02196-8
Heart rhythm complexity as predictors for the prognosis of end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis
Abstract
Background: Heart rhythm complexity, a measure of heart rate dynamics and a risk predictor in various clinical diseases, has not been systematically studied in patients with end-stage renal disease. The aim of this study is to investigate the heart rhythm complexity and its prognostic value for mortality in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Methods: To assess heart rhythm complexity and conventional heart rate variability measures, 4-h continuous electrocardiography for a retrospective cohort of 202 ostensibly healthy control subjects and 51 hemodialysis patients with end-stage renal disease were analyzed. Heart rhythm complexity was quantified by the complexity index from the measurement of the multiscale entropy profile.
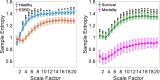
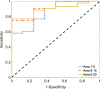
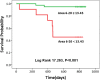
Results: During a follow-up of 13 months, 8 people died in the patient group. Values of either traditional heart rate variability measurements or complexity indices were found significantly lower in patients than those in healthy controls. In addition, the complexity indices (Area 1-5, Area 6-15 and Area 6-20) in the mortality group were significantly lower than those in the survival group, while there were no significant differences in traditional heart rate variability parameters between the two groups. In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, Area 6-20 (AUC = 0.895, p < 0.001) showed the strongest predictive power between mortality and survival groups.
Conclusion: The results suggest that heart rhythm complexity is impaired for patients with end-stage renal disease. Furthermore, the complexity index of heart rate variability quantified by multiscale entropy may be a powerful independent predictor of mortality in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Keywords: Autonomic nervous system; Complexity; End-stage renal disease; Heart rate variability; Multiscale entropy.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Wetmore JB, Collins AJ. Global challenges posed by the growth of end-stage renal disease. Ren Replace Ther. 2016;2:15. doi: 10.1186/s41100-016-0021-7. - DOI
-
- Chandra P, Sands RL, Gillespie BW, Levin NW, Kotanko P, Kiser M, Finkelstein F, Hinderliter A, Pop-Busui R, Rajagopalan S, Saran R. Predictors of heart rate variability and its prognostic significance in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(2):700–709. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr340. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

