Exercise enhances: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial on aerobic exercise as depression treatment augmentation
- PMID: 33298013
- PMCID: PMC7724825
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-020-02989-z
Exercise enhances: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial on aerobic exercise as depression treatment augmentation
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a considerable public health concern. In spite of evidence-based treatments for MDD, many patients do not improve and relapse is common. Therefore, improving treatment outcomes is much needed and adjunct exercise treatment may have great potential. Exercise was shown to be effective as monotherapy for depression and as augmentation strategy, with evidence for increasing neuroplasticity. Data on the cost-effectiveness and the long-term effects of adjunct exercise treatment are missing. Similarly, the cognitive pathways toward remission are not well understood.
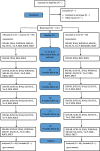
Methods: The present study is designed as a multicenter randomized superiority trial in two parallel groups with follow-up assessments up to 15 months. Currently depressed outpatients (N = 120) are randomized to guideline concordant Standard Care (gcSC) alone or gcSC with adjunct exercise treatment for 12 weeks. Randomization is stratified by gender and setting, using a four, six, and eight block design. Exercise treatment is offered in accordance with the NICE guidelines and empirical evidence, consisting of one supervised and two at-home exercise sessions per week at moderate intensity. We expect that gcSC with adjunct exercise treatment is more (cost-)effective in decreasing depressive symptoms compared to gcSC alone. Moreover, we will investigate the effect of adjunct exercise treatment on other health-related outcomes (i.e. functioning, fitness, physical activity, health-related quality of life, and motivation and energy). In addition, the mechanisms of change will be studied by exploring any change in rumination, self-esteem, and memory bias as possible mediators between exercise treatment and depression outcomes.
Discussion: The present trial aims to inform the scientific and clinical community about the (cost-)effectiveness and psychosocial mechanisms of change of adjunct exercise treatment when implemented in the mental health service setting. Results of the present study may improve treatment outcomes in MDD and facilitate implementation of prescriptive exercise treatment in outpatient settings.
Trial registration: This trial is registered within the Netherlands Trial Register (code: NL8432 , date: 6th March, 2020).
Keywords: (cost-)effectiveness; Depression; Exercise; RCT; Treatment augmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- GBD Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Correll CU, Solmi M, Veronese N, Bortolato B, Rosson S, Santonastaso P, et al. Prevalence, incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease in patients with pooled and specific severe mental illness: a large scale meta-analysis of 3,211,768 patients and 113,383,368 controls. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(2):163–180. doi: 10.1002/wps.20420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Depression [updated 2020, Jan 30; cited 2020, Aug 10]. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources