Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with serotonin syndrome
- PMID: 33298478
- PMCID: PMC7733117
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236450
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with serotonin syndrome
Abstract
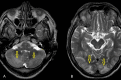
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a drug-induced clinical syndrome, characterised by a triad of cognitive impairment, autonomic hyperactivity and neuromuscular abnormalities. Hypertension, one of the common autonomic manifestations in SS, may lead to lead to several life-threatening conditions. Herein, we report a case of SS who had posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) because of high blood pressure.A young male with a 5-month history of chronic tension-type headache and depression had been receiving amitriptyline and paroxetine. Increment of paroxetine led to the development of various new clinical features, fulfilling the Hunter criteria of SS. MRI brain revealed high-signal intensity lesions on T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, and T2-weighted imaging in the posterior regions of the occipital, parietal, temporal and cerebellum lobes, suggestive of PRES. The patient responded to cyproheptadine. Autonomic hyperactivity, due to SS, is the most likely explanation of this association.
Keywords: drugs misuse (including addiction); neuro ITU; unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.J Clin Neurosci. 2011 Mar;18(3):406-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2010.06.011. Epub 2011 Jan 14. J Clin Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21236681
-
Generalised reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a variant of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Nov 26;2015:bcr2015210498. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-210498. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26611477 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Magnetic resonance imaging findings with emphasis on increased leptomeningeal FLAIR signal.Neuroradiol J. 2015 Dec;28(6):638-43. doi: 10.1177/1971400915609338. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Neuroradiol J. 2015. PMID: 26515749 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in nephrotic syndrome: case report and review of the literature.Clin Nephrol. 2012 Nov;78(5):406-11. doi: 10.5414/cn106976. Clin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23084334 Review.
-
Variant Type of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Associated with Deep Brain Hemorrhage: Case Report and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2020 Feb;134:176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.196. Epub 2019 Nov 8. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31712110 Review.
Cited by
-
Antidepressant Drugs Effects on Blood Pressure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 3;8:704281. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.704281. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34414219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin syndrome presenting as acute dizziness with supine hypertension and orthostatic hypotension.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Apr 16;17(4):e260229. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2024-260229. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38627042
-
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Induced by Mirtazapine Overdose: A Case Report.Case Rep Neurol Med. 2025 Jun 6;2025:4690032. doi: 10.1155/crnm/4690032. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2025. PMID: 40519857 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
