Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission
- PMID: 33298944
- PMCID: PMC7726563
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6
Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission
Abstract
Anecdotal evidence suggests that Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, exhibits differences in morbidity and mortality between sexes. Here, we present a meta-analysis of 3,111,714 reported global cases to demonstrate that, whilst there is no difference in the proportion of males and females with confirmed COVID-19, male patients have almost three times the odds of requiring intensive treatment unit (ITU) admission (OR = 2.84; 95% CI = 2.06, 3.92) and higher odds of death (OR = 1.39; 95% CI = 1.31, 1.47) compared to females. With few exceptions, the sex bias observed in COVID-19 is a worldwide phenomenon. An appreciation of how sex is influencing COVID-19 outcomes will have important implications for clinical management and mitigation strategies for this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

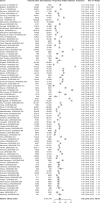


References
-
- Singh, S., Chowdhry, M., Chatterjee, A. & Khan, A. Gender-Based Disparities in COVID-19: Clinical Characteristics and Propensity-matched Analysis of Outcomes. medRxiv10.1101/2020.04.24.20079046 (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

