Lymphoangiocrine signals promote cardiac growth and repair
- PMID: 33299187
- PMCID: PMC7770123
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2998-x
Lymphoangiocrine signals promote cardiac growth and repair
Abstract
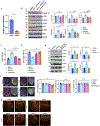
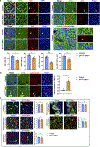
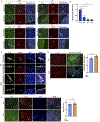
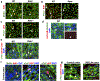
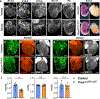
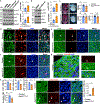
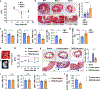
Recent studies have suggested that lymphatics help to restore heart function after cardiac injury1-6. Here we report that lymphatics promote cardiac growth, repair and cardioprotection in mice. We show that a lymphoangiocrine signal produced by lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) controls the proliferation and survival of cardiomyocytes during heart development, improves neonatal cardiac regeneration and is cardioprotective after myocardial infarction. Embryos that lack LECs develop smaller hearts as a consequence of reduced cardiomyocyte proliferation and increased cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Culturing primary mouse cardiomyocytes in LEC-conditioned medium increases cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival, which indicates that LECs produce lymphoangiocrine signals that control cardiomyocyte homeostasis. Characterization of the LEC secretome identified the extracellular protein reelin (RELN) as a key component of this process. Moreover, we report that LEC-specific Reln-null mouse embryos develop smaller hearts, that RELN is required for efficient heart repair and function after neonatal myocardial infarction, and that cardiac delivery of RELN using collagen patches improves heart function in adult mice after myocardial infarction by a cardioprotective effect. These results highlight a lymphoangiocrine role of LECs during cardiac development and injury response, and identify RELN as an important mediator of this function.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
JH is a shareholder of Reelin Therapeutics and a coinventor on a pending US patent application filed by his institution (UT Southwestern; application number 15/763,047 and publication number 20180273637, title “Methods and Compositions for Treatment of Atherosclerosis”; Inventors: Joachim Herz, Yinyuan Ding, Xunde Xian, Linzhang Huang, Chieko Mineo, Philip Shaul, Laurent Calvier). This patent application covers no aspects of the current manuscript. Findings regarding the potential applications and methods for using Reelin to treat cardiac diseases are the subject of provisional patent application US 63/091,558 owned by Northwestern University and list X.L. and G.O. as inventors. The rest of the authors declares no competing interests.
Figures

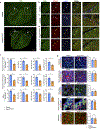

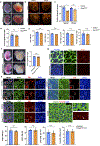
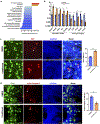
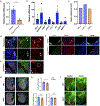


Comment in
-
Novel cardioprotective lymphatic signal identified.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Mar;18(3):150. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00495-z. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33349669 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vuorio T, Tirronen A & Ylä-Herttuala S Cardiac Lymphatics – A New Avenue for Therapeutics? Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 28, 285–296 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Henri O et al. Selective Stimulation of Cardiac Lymphangiogenesis Reduces Myocardial Edema and Fibrosis Leading to Improved Cardiac Function Following Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 133, 1484–97; discussion 1497 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS093382/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI112522/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD011996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM108569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL063762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR031680/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151388/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122309/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008061/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026814/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL134633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK114857/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025194/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

