Evaluation of the Effect of Hypericum triquetrifolium Turra on Memory Impairment Induced by Chronic Psychosocial Stress in Rats: Role of BDNF
- PMID: 33299301
- PMCID: PMC7720289
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S278153
Evaluation of the Effect of Hypericum triquetrifolium Turra on Memory Impairment Induced by Chronic Psychosocial Stress in Rats: Role of BDNF
Abstract
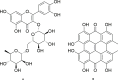
Background: Chronic psychosocial stress impairs memory function and leads to a depression-like phenotype induced by a persistent status of oxidative stress. Hypericum perforatum L. (St. John's wort) is widely used to relieve symptoms of anxiety and depression; however, its long-term use is associated with adverse effects. Hypericum triquetrifolium Turra is closely related to H. perforatum. Both plants belong to Hypericaceae family and share many biologically active compounds. Previous work by our group showed that methanolic extracts of H. triquetrifolium have potent antioxidant activity as well as high hypericin content, a component that proved to have stress-relieving and antidepressant effects by other studies. Therefore, we hypothesized that H. triquetrifolium would reduce stress-induced cognitive impairment in a rat model of chronic stress.
Objective: To determine whether chronic treatment with H. triquetrifolium protects against stress-associated memory deficits and to investigate a possible mechanism.
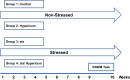
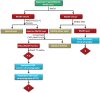
Methods: The radial arm water maze (RAWM) was used to test learning and memory in rats exposed to daily stress using the resident-intruder paradigm. Stressed and unstressed rats received chronic H. triquetrifolium or vehicle. We also measured levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum.
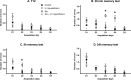
Results: Neither chronic stress nor chronic H. triquetrifolium administration affected performance during acquisition. However, memory tests in the RAWM showed that chronic stress impaired different post-encoding memory stages. H. triquetrifolium prevented this impairment. Furthermore, hippocampal BDNF levels were markedly lower in stressed animals than in unstressed animals, and chronic administration of H triquetrifolium chronic administration protected against this reduction. No significant difference was observed in the effects of chronic stress and/or H. triquetrifolium treatment on BDNF levels in the cerebellum and cortex.
Conclusion: H. triquetrifolium extract can oppose stress-associated hippocampus-dependent memory deficits in a mechanism that may involve BDNF in the hippocampus.
Keywords: BDNF; Hypericum triquetrifolium; hippocampus; learning; memory; methanolic extract; stress.
© 2020 Alzoubi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


References
-
- De Quervain D, Schwabe L, Roozendaal B. Stress, glucocorticoids and memory: implications for treating fear-related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:7–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

