Role of Muscarinic Receptors in Hypoalgesia Induced by Crocin in Neuropathic Pain Rats
- PMID: 33299384
- PMCID: PMC7710400
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4046256
Role of Muscarinic Receptors in Hypoalgesia Induced by Crocin in Neuropathic Pain Rats
Abstract
Objective: Crocin as an important constituent of saffron has antineuropathic pain properties; however, the exact mechanism of this effect is not known. The aim of this study was whether the hypoalgesic effect of crocin can be exerted through muscarinic receptors.
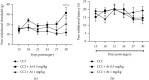
Materials and methods: In the present project, 36 male Wistar rats (200 ± 20 g) were used. Animals randomly divided into six groups (sham, neuropathy, neuropathy + crocin, neuropathy + atropine 0.5 mg/kg, neuropathy + atropine 1 mg/kg, and neuropathy + atropine 1 mg/kg + crocin). Neuropathy was induced by the chronic constriction injury (CCI) method on the sciatic nerve. Crocin and atropine was administered intraperitoneally during 14 days following the 14th day after surgery. Pain response was detected every three days, two hours after each injection and 3 days following last injection. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were detected using the Von Frey filaments and plantar test device, respectively.
Results: CCI significantly reduced the paw withdrawal response to mechanical and thermal stimulus (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively). Crocin therapy significantly reduced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia induced by CCI (P < 0.05). Atropine pretreatment significantly blocked the hypoalgesic effect of crocin (P < 0.05 in mechanical allodynia and P < 0.01 in thermal hyperalgesia). Fourteen days administration of atropine alone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg but not 1 mg/kg significantly reduced CCI-induced mechanical allodynia at day 30 after surgery.
Conclusion: Crocin significantly decreased CCI-induced neuropathic pain. The hypoalgesic effect of crocin was blocked by atropine pretreatment, which indicates an important role for muscarinic receptors in the effect of crocin.
Copyright © 2020 Hossein Ali Safakhah et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ferrier J., Bayet-Robert M., Dalmann R., et al. Cholinergic neurotransmission in the posterior insular cortex is altered in preclinical models of neuropathic pain: key role of muscarinic M2 receptors in donepezil-induced antinociception. Journal of Neuroscience. 2015;35(50):16418–16430. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.1537-15.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

