Azanitrile Inhibitors of the SmCB1 Protease Target Are Lethal to Schistosoma mansoni: Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Chemotype Reactivity
- PMID: 33301315
- PMCID: PMC7802074
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00644
Azanitrile Inhibitors of the SmCB1 Protease Target Are Lethal to Schistosoma mansoni: Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Chemotype Reactivity
Abstract
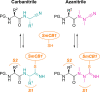
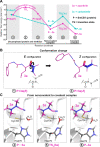
Azapeptide nitriles are postulated to reversibly covalently react with the active-site cysteine residue of cysteine proteases and form isothiosemicarbazide adducts. We investigated the interaction of azadipeptide nitriles with the cathepsin B1 drug target (SmCB1) from Schistosoma mansoni, a pathogen that causes the global neglected disease schistosomiasis. Azadipeptide nitriles were superior inhibitors of SmCB1 over their parent carba analogs. We determined the crystal structure of SmCB1 in complex with an azadipeptide nitrile and analyzed the reaction mechanism using quantum chemical calculations. The data demonstrate that azadipeptide nitriles, in contrast to their carba counterparts, undergo a change from E- to Z-configuration upon binding, which gives rise to a highly favorable energy profile of noncovalent and covalent complex formation. Finally, azadipeptide nitriles were considerably more lethal than their carba analogs against the schistosome pathogen in culture, supporting the further development of this chemotype as a treatment for schistosomiasis.
Keywords: azapeptide inhibitors; cysteine proteases; protein structures; schistosomiasis; structure−activity relationships.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeting SmCB1: Perspectives and Insights to Design Antischistosomal Drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(16):2264-2284. doi: 10.2174/0109298673255826231011114249. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37921174 Review.
-
Nature-Inspired Gallinamides Are Potent Antischistosomal Agents: Inhibition of the Cathepsin B1 Protease Target and Binding Mode Analysis.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 14;10(6):1935-1948. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00589. Epub 2024 May 17. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38757505 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable Hot Spots in the Schistosomiasis Cathepsin B1 Target Identified by Functional and Binding Mode Analysis of Potent Vinyl Sulfone Inhibitors.ACS Infect Dis. 2021 May 14;7(5):1077-1088. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00501. Epub 2020 Nov 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33175511 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Characterization of Schistosoma mansoni Cathepsin B1.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2151:145-158. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0635-3_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32452002
-
Induction of protective immune responses against schistosomiasis using functionally active cysteine peptidases.Front Genet. 2014 May 8;5:119. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00119. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24847355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting SmCB1: Perspectives and Insights to Design Antischistosomal Drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(16):2264-2284. doi: 10.2174/0109298673255826231011114249. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37921174 Review.
-
Schistosomiasis Drug Discovery in the Era of Automation and Artificial Intelligence.Front Immunol. 2021 May 31;12:642383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.642383. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nature-Inspired Gallinamides Are Potent Antischistosomal Agents: Inhibition of the Cathepsin B1 Protease Target and Binding Mode Analysis.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Jun 14;10(6):1935-1948. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00589. Epub 2024 May 17. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38757505 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma japonicum cathepsin L1: A potential target for anti-schistosomiasis strategies.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jul 7;19(7):e0013241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0013241. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40623040 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-Wide Profiling of the Covalent-Druggable Cysteines with a Structure-Based Deep Graph Learning Network.Research (Wash D C). 2022 Jul 21;2022:9873564. doi: 10.34133/2022/9873564. eCollection 2022. Research (Wash D C). 2022. PMID: 35958111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mir F. M.; Atmuri N. D. P.; Bourguet C. B.; Fores J. R.; Hou X.; Chemtob S.; Lubell W. D. (2019) Paired Utility of Aza-Amino Acyl Proline and Indolizidinone Amino Acid Residues for Peptide Mimicry: Conception of Prostaglandin F2alpha Receptor Allosteric Modulators That Delay Preterm Birth. J. Med. Chem. 62 (9), 4500–4525. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00056. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

