Endothelial S1P1 Signaling Counteracts Infarct Expansion in Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 33301355
- PMCID: PMC7874503
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316711
Endothelial S1P1 Signaling Counteracts Infarct Expansion in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
Rationale: Cerebrovascular function is critical for brain health, and endogenous vascular protective pathways may provide therapeutic targets for neurological disorders. S1P (Sphingosine 1-phosphate) signaling coordinates vascular functions in other organs, and S1P1 (S1P receptor-1) modulators including fingolimod show promise for the treatment of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. However, S1P1 also coordinates lymphocyte trafficking, and lymphocytes are currently viewed as the principal therapeutic target for S1P1 modulation in stroke.
Objective: To address roles and mechanisms of engagement of endothelial cell S1P1 in the naive and ischemic brain and its potential as a target for cerebrovascular therapy.
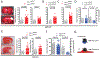
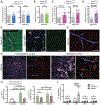
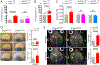
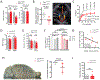
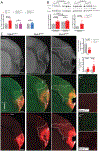
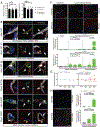
Methods and results: Using spatial modulation of S1P provision and signaling, we demonstrate a critical vascular protective role for endothelial S1P1 in the mouse brain. With an S1P1 signaling reporter, we reveal that abluminal polarization shields S1P1 from circulating endogenous and synthetic ligands after maturation of the blood-neural barrier, restricting homeostatic signaling to a subset of arteriolar endothelial cells. S1P1 signaling sustains hallmark endothelial functions in the naive brain and expands during ischemia by engagement of cell-autonomous S1P provision. Disrupting this pathway by endothelial cell-selective deficiency in S1P production, export, or the S1P1 receptor substantially exacerbates brain injury in permanent and transient models of ischemic stroke. By contrast, profound lymphopenia induced by loss of lymphocyte S1P1 provides modest protection only in the context of reperfusion. In the ischemic brain, endothelial cell S1P1 supports blood-brain barrier function, microvascular patency, and the rerouting of blood to hypoperfused brain tissue through collateral anastomoses. Boosting these functions by supplemental pharmacological engagement of the endothelial receptor pool with a blood-brain barrier penetrating S1P1-selective agonist can further reduce cortical infarct expansion in a therapeutically relevant time frame and independent of reperfusion.
Conclusions: This study provides genetic evidence to support a pivotal role for the endothelium in maintaining perfusion and microvascular patency in the ischemic penumbra that is coordinated by S1P signaling and can be harnessed for neuroprotection with blood-brain barrier-penetrating S1P1 agonists.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; collateral circulation; endothelium; fingolimod hydrochloride; neuroprotective agents; stroke.
Figures


Comment in
-
New Vistas in Stroke Treatment: Targeting the Endothelium to Restore Blood Flow.Circ Res. 2021 Feb 5;128(3):383-385. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318671. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33539221 No abstract available.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke. 2018;49:e46–e110 - PubMed
-
- Manning NW, Campbell BC, Oxley TJ, Chapot R. Acute ischemic stroke: Time, penumbra, and reperfusion. Stroke. 2014;45:640–644 - PubMed
-
- Bonnin P, Mazighi M, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Kubis N. Early collateral recruitment after stroke in infants and adults. Stroke. 2019;50:2604–2611 - PubMed
-
- Shuaib A, Butcher K, Mohammad AA, Saqqur M, Liebeskind DS. Collateral blood vessels in acute ischaemic stroke: A potential therapeutic target. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:909–921 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

