The Role of Copper (II) on Kininogen Binding to Tropomyosin in the Presence of a Histidine-Proline-Rich Peptide
- PMID: 33302425
- PMCID: PMC7762548
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249343
The Role of Copper (II) on Kininogen Binding to Tropomyosin in the Presence of a Histidine-Proline-Rich Peptide
Abstract
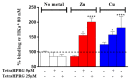
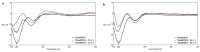
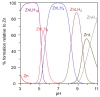
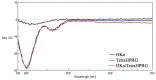
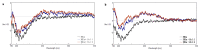
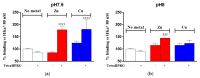
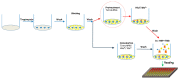
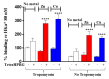
The antiangiogenic activity of the H/P domain of histidine-proline-rich glycoprotein is mediated by its binding with tropomyosin, a protein exposed on endothelial cell-surface during the angiogenic switch, in presence of zinc ions. Although it is known that copper ion serum concentration is significantly increased in cancer patients, its role in the interaction of H/P domain with tropomyosin, has not yet been studied. In this paper, by using ELISA assay, we determined the modulating effect of TetraHPRG peptide, a sequence of 20 aa belonging to H/P domain, on the binding of Kininogen (HKa) with tropomyosin, both in absence and presence of copper and zinc ions. A potentiometric study was carried out to characterize the binding mode adopted by metal ions with TetraHPRG, showing the formation of complex species involving imidazole amide nitrogen atoms in metal binding. Moreover, circular dichroism showed a conformational modification of ternary systems formed by TetraHPRG, HKa and copper or zinc. Interestingly, slight pH variation influenced the HKa-TetraHPRG-tropomyosin binding. All these results indicate that both metal ions are crucial in the interaction between TetraHPRG, tropomyosin and HKa.
Keywords: angiogenesis; circular dichroism; copper; histidine–proline-rich glycoprotein; kininogen; tropomyosin; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histidine-proline rich glycoprotein (HPRG) binds and transduces anti-angiogenic signals through cell surface tropomyosin on endothelial cells.Thromb Haemost. 2004 Aug;92(2):403-12. doi: 10.1160/TH04-02-0073. Thromb Haemost. 2004. PMID: 15269838
-
Peptides derived from the histidine-proline domain of the histidine-proline-rich glycoprotein bind to tropomyosin and have antiangiogenic and antitumor activities.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 15;64(16):5812-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0440. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15313924
-
Peptides derived from the histidine-proline rich glycoprotein bind copper ions and exhibit anti-angiogenic properties.Dalton Trans. 2018 Jul 17;47(28):9492-9503. doi: 10.1039/c8dt01560k. Dalton Trans. 2018. PMID: 29963662
-
Inhibition of angiogenesis by cleaved high molecular weight kininogen (HKa) and HKa domain 5.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005 Nov;5(7):519-28. doi: 10.2174/156800905774574039. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 16305348 Review.
-
Extracellular tropomyosin: a novel common pathway target for anti-angiogenic therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004 Nov;4(7):543-53. doi: 10.2174/1568009043332781. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 15578912 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Advances in the Role of the Tropomyosin Family in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 27;24(17):13295. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713295. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal Complexes in Diagnosis and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4377. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084377. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lijnen H.R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Heparin binding properties of human histidine-rich glycoprotein. Mechanism and role in the neutralization of heparin in plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 1983;258:3803–3808. - PubMed
-
- Lijnen H.R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Isolation and characterization of a human plasma protein with affinity for the lysine binding sites in plasminogen. Role in the regulation of fibrinolysis and identification as histidine-rich glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:10214–10222. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

