Cooperation and Interplay between EGFR Signalling and Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis in Cancer
- PMID: 33302515
- PMCID: PMC7764760
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9122639
Cooperation and Interplay between EGFR Signalling and Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis in Cancer
Abstract
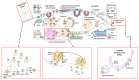
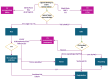
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) takes centre stage in carcinogenesis throughout its entire cellular trafficking odyssey. When loaded in extracellular vesicles (EVs), EGFR is one of the key proteins involved in the transfer of information between parental cancer and bystander cells in the tumour microenvironment. To hijack EVs, EGFR needs to play multiple signalling roles in the life cycle of EVs. The receptor is involved in the biogenesis of specific EV subpopulations, it signals as an active cargo, and it can influence the uptake of EVs by recipient cells. EGFR regulates its own inclusion in EVs through feedback loops during disease progression and in response to challenges such as hypoxia, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and drugs. Here, we highlight how the spatiotemporal rules that regulate EGFR intracellular function intersect with and influence different EV biogenesis pathways and discuss key regulatory features and interactions of this interplay. We also elaborate on outstanding questions relating to EGFR-driven EV biogenesis and available methods to explore them. This mechanistic understanding will be key to unravelling the functional consequences of direct anti-EGFR targeted and indirect EGFR-impacting cancer therapies on the secretion of pro-tumoural EVs and on their effects on drug resistance and microenvironment subversion.
Keywords: EV biogenesis; EV heterogeneity; MVB heterogeneity; endocytosis; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); extracellular vesicles (EVs); microenvironment subversion; therapy resistance; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
S.E.B. has equity in Evox Therapeutics Ltd. and holds an ongoing contract with Evox Therapeutics Ltd. from 2017 to present. Evox Therapeutics Ltd. had no influence on the conception or realisation of this review.
Figures
References
-
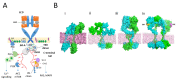
- Needham S.R., Roberts S.K., Arkhipov A., Mysore V.P., Tynan C.J., Zanetti-Domingues L.C., Kim E.T., Losasso V., Korovesis D., Hirsch M., et al. EGFR oligomerization organizes kinase-active dimers into competent signalling platforms. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:13307. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zanetti-Domingues L.C., Korovesis D., Needham S.R., Tynan C.J., Sagawa S., Roberts S.K., Kuzmanic A., Ortiz-Zapater E., Jain P., Roovers R.C., et al. The architecture of EGFR’s basal complexes reveals autoinhibition mechanisms in dimers and oligomers. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:4325. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06632-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

