Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) with Focus on Brain and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33302545
- PMCID: PMC7764580
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249357
Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) with Focus on Brain and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
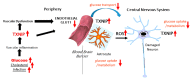
The development of new therapeutic approaches to diseases relies on the identification of key molecular targets involved in amplifying disease processes. One such molecule is thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), also designated thioredoxin-binding protein-2 (TBP-2), a member of the α-arrestin family of proteins and a central regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, involved in diabetes-associated vascular endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. TXNIP sequesters reduced thioredoxin (TRX), inhibiting its function, resulting in increased oxidative stress. Many different cellular stress factors regulate TXNIP expression, including high glucose, endoplasmic reticulum stress, free radicals, hypoxia, nitric oxide, insulin, and adenosine-containing molecules. TXNIP is also directly involved in inflammatory activation through its interaction with the nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, and pyrin domain-containing-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome complex. Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease have significant pathologies associated with increased oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular dysfunctions. In addition, as dysfunctions in glucose and cellular metabolism have been associated with such brain diseases, a role for TXNIP in neurodegeneration has actively been investigated. In this review, we will focus on the current state of the understanding of possible normal and pathological functions of TXNIP in the central nervous system from studies of in vitro neural cells and the brains of humans and experimental animals with reference to other studies. As TXNIP can be expressed by neurons, microglia, astrocytes, and endothelial cells, a complex pattern of regulation and function in the brain is suggested. We will examine data suggesting TXNIP as a therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases where further research is needed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; glucose metabolism; inflammation; neuropathology; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- López-Contreras A.K., Martínez-Ruiz M.G., Olvera-Montaño C., Robles-Rivera R.R., Arévalo-Simental D.E., Castellanos-González J.A., Hernández-Chávez A., Huerta-Olvera S.G., Cardona-Muñoz E.G., Rodríguez-Carrizalez A.D. Importance of the Use of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Inflammatory Profile in Aqueous and Vitreous Humor in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants. 2020;9:891. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090891. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

