AFM Analysis of Micron and Sub-Micron Sized Bridges Fabricated Using the Femtosecond Laser on YBCO Thin Films
- PMID: 33302556
- PMCID: PMC7764433
- DOI: 10.3390/mi11121088
AFM Analysis of Micron and Sub-Micron Sized Bridges Fabricated Using the Femtosecond Laser on YBCO Thin Films
Abstract
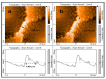
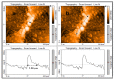
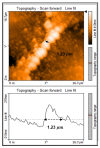
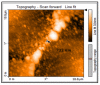
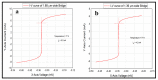
The research arose as a result of the need to use the femtosecond laser to fabricate sub-micron and nano-sized bridges that could be analyzed for the Josephson effect. The femtosecond laser has a low pulse duration of 130 femtoseconds. Hence in an optical setup it was assumed that it could prevent the thermal degradation of the superconductive material during fabrication. In this paper a series of micron and sub-micron sized bridges where fabricated on superconductive yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) thin film using the femtosecond laser, a spherical convex lens of focal length 30 mm and the G-code control programming language applied to a translation stage. The dimensions of the bridges fabricated where analyzed using the atomic force microscope (AFM). As a result, micron sized superconductive bridges of width 1.68 μm, 1.39 μm, 1.23 μm and sub-micron sized bridges of width 858 nm, 732 nm where fabricated. The length of this bridges ranged from 9.6 μm to 12.8 μm. The femtosecond laser technique and the spherical convex lens can be used to fabricate bridges in the sub-micron dimension.
Keywords: YBCO thin film; atomic force microscope; laser ablation diameter; separation distance (SW); sub-micron bridges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vogel A., Noack J., Huttman G., Paltauf G. Mechanisms of femtosecond laser nanosurgery of cells and tissues. Appl. Phys. B. 2005;81:1015–1047. doi: 10.1007/s00340-005-2036-6. - DOI
-
- Yao J., Zhang C., Liu H., Dai Q., Wu L., Lan S., Gopal A.V., Trofimov V.A., Lysak T.M. Selective appearance of several laser-induced periodic surface structure patterns on a metal surface using structural colors produced by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012;258:7625–7632. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.04.105. - DOI
-
- Wang S.Y., Ren Y., Cheng C.W., Chen J.K., Tzou D.Y. Micromachining of copper by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013;265:302–308. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.200. - DOI
-
- Bian Q., Yu X., Zhao B., Chang Z., Lei S. Femtosecond laser ablation of indium tin-oxide narrow grooves for thin film solar cells. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013;45:395–401. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.06.018. - DOI
-
- Campbell T.A., Haugan T.J., Maartense I., Murphy J., Brunke L., Barnes P.N. Flux pinning effects of Y2O3 nanoparticulate dispersions in multilayered YBCO thin films. Phys. C. 2005;423:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2004.09.018. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

