Capsaicin, a Powerful •OH-Inactivating Ligand
- PMID: 33302572
- PMCID: PMC7763808
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9121247
Capsaicin, a Powerful •OH-Inactivating Ligand
Abstract
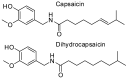
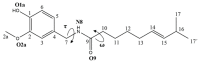
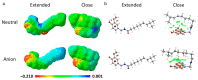
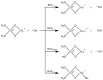
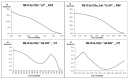
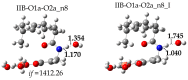
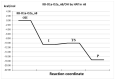
Oxidative conditions are frequently enhanced by the presence of redox metal ions. In this study, the role of capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide, CAP) in copper-induced oxidative stress was investigated using density functional theory simulations. It was found that CAP has the capability to chelate Cu(II), leading to complexes that are harder to reduce than free Cu(II). CAP fully turns off the Cu(II) reduction by Asc-, and slows down the reduction in this cation by O2•-. Therefore, CAP is proposed as an •OH-inactivating ligand by impeding the reduction in metal ions (OIL-1), hindering the production of •OH via Fenton-like reactions, at physiological pH. CAP is also predicted to be an excellent antioxidant as a scavenger of •OH, yielded through Fenton-like reactions (OIL-2). The reactions between CAP-Cu(II) chelates and •OH were estimated to be diffusion-limited. Thus, these chelates are capable of deactivating this dangerous radical immediately after being formed by Fenton-like reactions.
Keywords: Cu-complexes; DFT; capsaicin; fenton reaction; molecular dynamics; natural antioxidant; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. [(accessed on 3 July 2019)]; Available online: www.fao.org.
-
- Hayman M., Kam P.C.A. Capsaicin: A review of its pharmacology and clinical applications. Curr. Anaesth. Crit. Care. 2008;19:338–343. doi: 10.1016/j.cacc.2008.07.003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

