Cyanide Complexes Based on {Mo6I8}4+ and {W6I8}4+ Cluster Cores
- PMID: 33302595
- PMCID: PMC7764029
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25245796
Cyanide Complexes Based on {Mo6I8}4+ and {W6I8}4+ Cluster Cores
Abstract
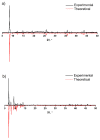
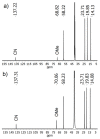
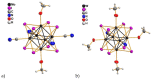
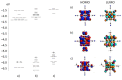
Compounds based on new cyanide cluster anions [{Mo6I8}(CN)6]2-, trans-[{Mo6I8}(CN)4(MeO)2]2- and trans-[{W6I8}(CN)2(MeO)4]2- were synthesized using mechanochemical or solvothermal synthesis. The crystal and electronic structures as well as spectroscopic properties of the anions were investigated. It was found that the new compounds exhibit red luminescence upon excitation by UV light in the solid state and solutions, as other cluster complexes based on {Mo6I8}4+ and {W6I8}4+ cores do. The compounds can be recrystallized from aqueous methanol solutions; besides this, it was shown using NMR and UV-Vis spectroscopy that anions did not undergo hydrolysis in the solutions for a long time. These facts indicate that hydrolytic stabilization of {Mo6I8} and {W6I8} cluster cores can be achieved by coordination of cyanide ligands.
Keywords: cluster compounds; crystal structure; cyanide ligand; hydrolytic stability; luminescence; molybdenum; tungsten.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sokolov M.N., Brylev K.A., Abramov P.A., Gallyamov M.R., Novozhilov I.N., Kitamura N., Mikhaylov M.A. Complexes of {W6I8}4+ Clusters with Carboxylates: Preparation, Electrochemistry, and Luminescence. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017;2017:4131–4137. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201700618. - DOI
-
- Seyboldt A., Enseling D., Jüstel T., Ivanović M., Peisert H., Chassé T., Meyer H.-J. Ligand Influence on the Photophysical Properties and Electronic Structures of Tungsten Iodide Clusters. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017;2017:5387–5394. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201700910. - DOI
-
- Kirakci K., Fejfarová K., Kučeráková M., Lang K. Hexamolybdenum Cluster Complexes with Pyrene and Anthracene Carboxylates: Ultrabright Red Emitters with the Antenna Effect. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014;2014:2331–2336. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201402076. - DOI
-
- Zietlow T.C., Nocera D.G., Gray H.B. Photophysics and Electrochemistry of Hexanuclear Tungsten Halide Clusters. Inorg. Chem. 1986;25:1351–1353. doi: 10.1021/ic00229a011. - DOI
-
- Maverick A.W., Najdzionek J.S., MacKenzie D., Nocera D.G., Gray H.B. Spectroscopic, Electrochemical, and Photochemical Properties of Molybdenum(II) and Tungsten(II) Halide Clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983;105:1878–1882. doi: 10.1021/ja00345a034. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

