Semaphorin 3A mediated brain tumor stem cell proliferation and invasion in EGFRviii mutant gliomas
- PMID: 33302912
- PMCID: PMC7727139
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07694-4
Semaphorin 3A mediated brain tumor stem cell proliferation and invasion in EGFRviii mutant gliomas
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common primary brain tumor in adults, with a median survival of approximately 15 months. Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), known for its axon guidance and antiangiogenic properties, has been implicated in GBM growth. We hypothesized that Sema3A directly inhibits brain tumor stem cell (BTSC) proliferation and drives invasion via Neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) and Plexin A1 (PlxnA1) receptors.
Methods: GBM BTSC cell lines were assayed by immunostaining and PCR for levels of Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) and its receptors Nrp1 and PlxnA1. Quantitative BrdU, cell cycle and propidium iodide labeling assays were performed following exogenous Sema3A treatment. Quantitative functional 2-D and 3-D invasion assays along with shRNA lentiviral knockdown of Nrp1 and PlxnA1 are also shown. In vivo flank studies comparing tumor growth of knockdown versus control BTSCs were performed. Statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism v7.
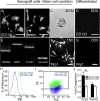
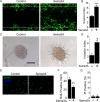
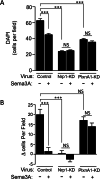
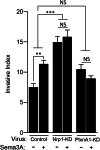
Results: Immunostaining and PCR analysis revealed that BTSCs highly express Sema3A and its receptors Nrp1 and PlxnA1, with expression of Nrp1 in the CD133 positive BTSCs, and absence in differentiated tumor cells. Treatment with exogenous Sema3A in quantitative BrdU, cell cycle, and propidium iodide labeling assays demonstrated that Sema3A significantly inhibited BTSC proliferation without inducing cell death. Quantitative functional 2-D and 3-D invasion assays showed that treatment with Sema3A resulted in increased invasion. Using shRNA lentiviruses, knockdown of either NRP1 or PlxnA1 receptors abrogated Sema3A antiproliferative and pro-invasive effects. Interestingly, loss of the receptors mimicked Sema3A effects, inhibiting BTSC proliferation and driving invasion. Furthermore, in vivo studies comparing tumor growth of knockdown and control infected BTSCs implanted into the flanks of nude mice confirmed the decrease in proliferation with receptor KD.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate the importance of Sema3A signaling in GBM BTSC proliferation and invasion, and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Brain tumor stem cells; Glioma; Neuropilin; Plexin; Semaphorin.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autocrine semaphorin 3A signaling promotes glioblastoma dispersal.Oncogene. 2009 Oct 8;28(40):3537-50. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.204. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19684614
-
Plexin A1 signaling confers malignant phenotypes in lung cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Nov 4;480(1):75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27717823
-
The semaphorin 3A/neuropilin-1 pathway promotes clonogenic growth of glioblastoma via activation of TGF-β signaling.JCI Insight. 2023 Nov 8;8(21):e167049. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.167049. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37788099 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of semaphorin-mediated axon guidance.J Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;44(2):219-29. doi: 10.1002/1097-4695(200008)44:2<219::aid-neu11>3.0.co;2-w. J Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10934324 Review.
-
Integrative analysis of cell adhesion molecules in glioblastoma identified prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor (PTGFRN) as an essential gene.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 11;22(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09682-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35690717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Nervous System Development Regulator Neuropilin-1 as a Potential Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Brain Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4922. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204922. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cells-derived SEMA3G suppresses glioblastoma stem cells by inducing c-Myc degradation.Cell Death Differ. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1038/s41418-025-01534-3. Online ahead of print. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 40533501
-
Hallmarks of perineural invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: new biological dimensions.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 25;14:1421067. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1421067. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39119085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HNF4G accelerates glioma progression by facilitating NRP1 transcription.Oncol Lett. 2023 Feb 1;25(3):102. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13688. eCollection 2023 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36817051 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Mechanism of Combined Hydroxychavicol With Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Against Glioma Cancer Cell Lines: A Transcriptomic Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 22;13:844199. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.844199. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35392560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg MS. Handbook of neurosurgery. 7 th. 2006.
-
- Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Aster JC. Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of disease E-book. 2009.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

