Moving up the On-Site Sanitation ladder in urban India through better systems and standards
- PMID: 33303251
- PMCID: PMC7816121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111656
Moving up the On-Site Sanitation ladder in urban India through better systems and standards
Abstract
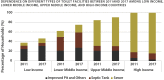
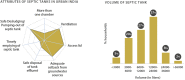
Wastewater management predominantly takes the form of On-Site Sanitation (OSS) in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LMICs). In India, households construct and operate OSS systems in the absence of regulatory oversight and seldom in compliance with the national technical standards - posing a risk to water sources and public health. The present paper reviews novel evidence on the quality of these systems from a multi-state survey of 3000 households in India to identify policy and practice interventions for creating sustainable urban sanitation futures. The paper argues for local and national governments to unlock the potential of OSS as a safe and long-term wastewater management solution through (1) re-envisioning the system design to simultaneously meet household and environmental needs, (2) fostering prefabrication of systems as a means to distribute the compliance responsibility optimally, and (3) updating technical standards for facilitating such a paradigm shift.
Keywords: India; On-site Sanitation; Prefabrication; Public health; Regulation; Septic tanks; Standards; Water pollution.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal N., Karunanithi A., Dwivedi A. 2020. Reuse and Recyling of Faecal-Sludge Derived Biosolids in Agriculture. New Delhi. - DOI
-
- Arwenyo B., Wasswa J., Nyeko M., Kasozi G.N. The impact of septic systems density and nearness to spring water points, on water quality. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017;11:11–18. doi: 10.5897/AJEST2016.2216. - DOI
-
- Bancalari A., Martinez S. Exposure to sewage from on-site sanitation and child health: a spatial analysis of linkages and externalities in peri-urban Bolivia. J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2018;8:90–99. doi: 10.2166/washdev.2017.179. - DOI
-
- Bhallamudi S.M., Kaviyarasan R., Abilarasu A., Philip L. Nexus between sanitation and groundwater quality: case study from a hard rock region in India. J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019;9:703–713. doi: 10.2166/washdev.2019.002. - DOI
-
- Bicki T.J., Brown R.B. On-Site Sewage Disposal: The influence of system density on water quality. J. Environ. Health. 1991;53(5):39–42. http://www.jstor.org/stable/44540392
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

